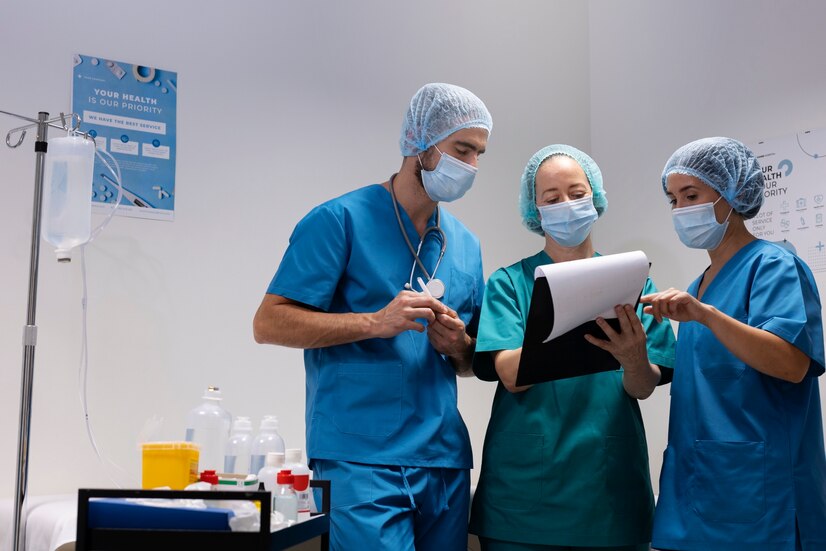
The healthcare industry has been under significant pressure in recent years. Healthcare systems around the world were stretched to breaking point during the recent pandemic, with hospital beds at capacity and staff working to exhaustion to cope with the growing influx of patients. It is little surprise that lockdowns and movement restrictions were put in place during this period, as there was a need to slow the spread of the virus to protect key healthcare infrastructure.
Today, as 2023 draws to a close, the systemic pressures brought on by COVID-19 may have lessened, but new challenges remain. Winter is a time of high demand across the healthcare economy. Viruses are more common, and accidents relating to poor weather (such as snow and ice) increase. However, some key developments in the wider healthcare industry have sought to modernize services and improve patient outcomes. This article outlines two of these developments.
1. Private ambulance services
As pressures mount on healthcare services, with increasing demand for emergency and non-emergency pre-hospital care there is a need to ensure that existing systems can cope with continuous high levels of demand. In recent years, many countries have been unable to meet government response time targets for both emergencies and non-life-threatening medical situations. As such, there has been a rise in the use of private ambulance services to cope with increased demand and ensure that timely responses to emergencies and routine hospital appointments can be achieved.
Today, many healthcare providers and commissioners rely on supplementing their existing ambulance fleet with privately run ambulance services. Companies in this sector commonly kit out civilian vehicles for pre-hospital services by “upfitting” them with equipment supplied by sites. Such companies supply essential vehicle equipment such as lights and sirens (used when private ambulance firms respond to emergencies) and window tinting kits to ensure patient privacy when transported in the back of an ambulance.
These suppliers help to ensure that private ambulance services are fit for purpose and provide a service that is similar to nationally run pre-hospital care. In short, as demand for transport to routine hospital appointments grows along with the need to respond quickly to emergencies, private ambulance services will form an increasingly important part of healthcare service delivery.
2. The rise of remote healthcare
Thanks to the continued growth and increasing adoption of internet-based services, healthcare providers can now provide a range of services by using telemedicine in primary care, telehealth, and telecare. These names are given to different aspects of healthcare, such as patient monitoring, holding patient assessments, and improving patient safety. The common factor in all these services is that remote support, consultation, or assessment is provided by using a range of tech devices and the internet.
For example, patients can use a range of wearable devices that record key health information (such as blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and blood sugar levels). This information is sent in real time over the internet to healthcare providers to allow remote monitoring to take place. Along with remote health consultations (via video conferencing apps), healthcare staff can deal with more patients without needing to travel.
ALSO READ: AI in Healthcare: AIOtechnical.com’s Innovative Approach