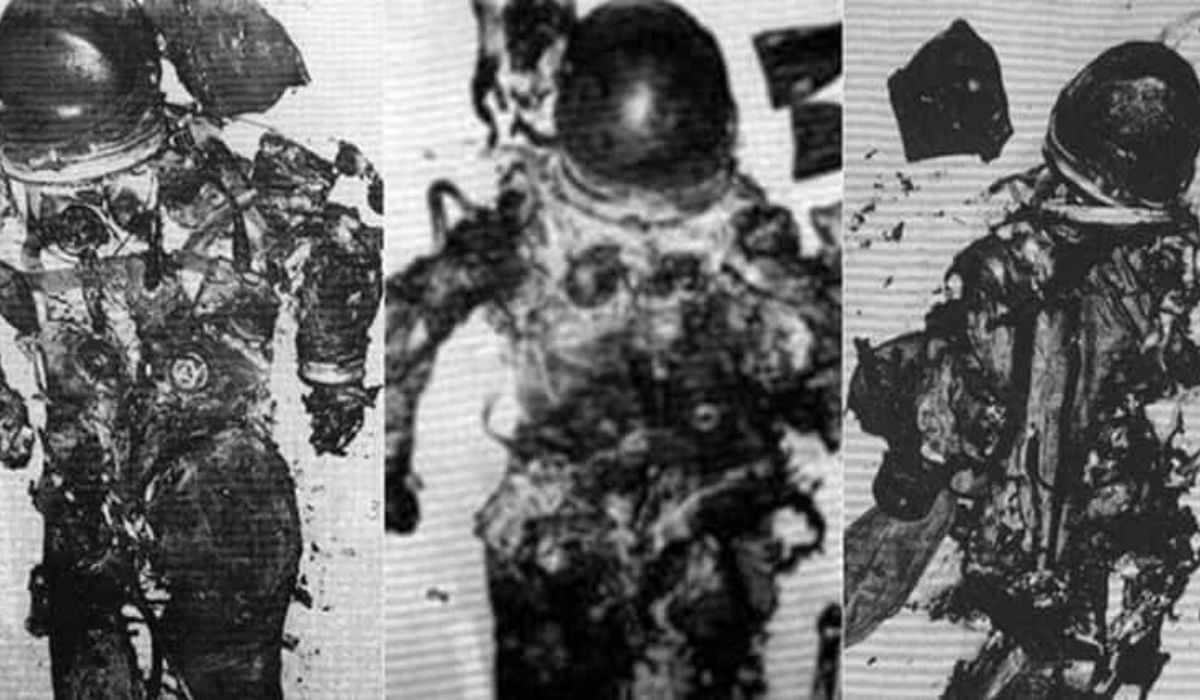
The Apollo 1 mission will forever be remembered as the terrible failure of a pre-launch test that claimed the lives of three men. This article apollo 1 bodies investigates the disaster, its fallout, and the legacy it left on space travel.
Historical context of the Apollo 1 mission
The historical setting of the Apollo 1 mission is crucial to comprehend before getting into the incident itself. To successfully place humans on the Moon and return them to Earth was a major goal of NASA’s Apollo mission.
The tragic accident and its aftermath
On January 27, 1967, three astronauts—Gus Grissom, Ed White, and Roger B. Chaffee—perished in a cabin fire during a pre-launch test for Apollo 1. This tragic event marked a low point in humankind’s exploration into space.
Understanding the cause of the accident
The terrible incident aboard the spaceship was traced back to electrical problems and combustible components. This in-depth evaluation made possible new standards in spaceship security.
Lessons learned and improvements in space safety
To ensure the safety of astronauts on future missions, strict safety precautions were taken after the Apollo 1 catastrophe. These efforts included the use of more fire-resistant materials, improved safety processes, and altered testing procedures.
Apollo program continuation and achievements
With the lessons learned from the Apollo 1 disaster, NASA pressed on with the Apollo program and eventually landed humans on the Moon during the successful Apollo 11 mission.
Remembering the Apollo 1 crew
As a constant reminder of the dangers and difficulties of space travel and the bravery of those who journey into the unknown, the Apollo 1 crew of Grissom, White, and Chaffee is honored to this day.
The importance of space exploration
As a sobering reminder of the significance of space travel, Apollo 1 encourages us to keep pushing the limits of our understanding of the universe.
Impact on future space missions
Safety, careful planning, and cutting-edge technology are all aspects of modern space missions that have been influenced by the lessons acquired during Apollo 1.
Advancements in astronaut safety measures
Improved spaceship architecture and life-support systems are just two examples of the many ways in which astronaut safety has progressed since Apollo 1.
Commemorating Apollo 1
NASA and the world community observe the Apollo 1 tragedy every year on January 27 to remember the three astronauts who perished in the accident and to renew their dedication to risk-free space travel.
Public perception and remembrance
The Apollo 1 accident influenced public opinion, creating a somber atmosphere and encouraging future generations to work in space exploration and safety.
The legacy of Apollo 1
Space exploration has continued to progress as a result of the lessons learned from Apollo 1, which is a monument to the human spirit.
Conclusion
As a reminder of the dangers and costs of space travel, the Apollo 1 disaster has lasting significance. However, it also sparked important innovations that ensured the success of future apollo 1 bodies space missions and made them safer for astronauts.
FAQs
Was Apollo 1 the first mission of the Apollo program?
Apollo 1 was not a pre-launch test for a future mission. Apollo 7 was the first Apollo mission to include humans.
What were the names of the Apollo 1 astronauts?
Astronauts Gus Grissom, Ed White, and Roger B. Chaffee made up the Apollo 1 crew.
How did the Apollo program change after the Apollo 1 incident?
Numerous precautions were taken to ensure the Apollo program’s success, such as improved fire safety procedures, rigorous testing, and refined spacecraft design.
Were there any other fatal accidents during the Apollo program?
The deadly accident on Apollo 1 was the only one during the whole Apollo program. There were no fatalities on any of the subsequent Apollo flights.
How did the Apollo 1 incident impact public perception of space exploration?
The Apollo 1 disaster brought to light the dangers of space travel, leading to a review of safety protocols and raising general awareness of the difficulties astronauts face.