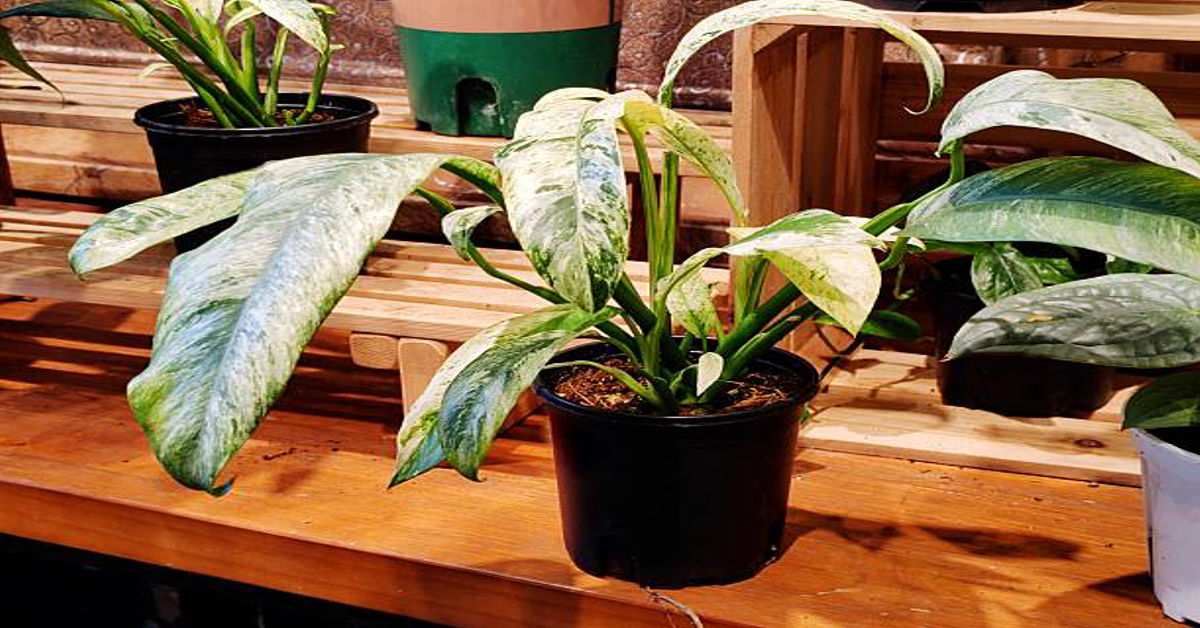
Tree philodendron is a striking tropical plant admired for its bold foliage, architectural form, and adaptability to indoor and outdoor environments. Unlike trailing or climbing philodendrons, this variety develops a self-supporting, upright structure that resembles a small tree over time. Its large, deeply lobed leaves and robust stems make it a favorite among plant enthusiasts, landscapers, and interior designers seeking a dramatic yet manageable plant. This comprehensive guide explores tree philodendron in depth, covering its botanical characteristics, growth habits, environmental needs, care routines, propagation methods, benefits, challenges, and long-term maintenance considerations.
Understanding the Tree Philodendron
Tree philodendron is a tropical evergreen plant known for its thick stems and expansive leaves that spread outward in a symmetrical, almost sculptural form. The term “tree philodendron” is commonly used to describe large, non-climbing philodendron species that grow upright rather than vining. These plants develop a sturdy trunk-like stem system as they mature, allowing them to stand independently without the need for support.
The leaves are the most defining feature of the tree philodendron. They are typically large, glossy, and deeply divided, giving them a dramatic, tropical appearance. Each leaf can grow to impressive dimensions under ideal conditions, contributing to the plant’s lush and commanding presence. The foliage is not only visually appealing but also plays a vital role in the plant’s ability to adapt to varying light levels.
Natural Habitat and Growth Behavior
In its natural environment, tree philodendron thrives in warm, humid regions where temperatures remain relatively stable throughout the year. It grows beneath taller trees, receiving filtered sunlight rather than direct exposure. This natural setting explains the plant’s tolerance for partial shade and its preference for indirect light.
Growth occurs steadily when conditions are favorable. The plant produces new leaves from a central growth point, and older leaves may gradually drop as part of the natural aging process. Over time, the base thickens, and aerial roots may appear, helping stabilize the plant and absorb moisture from the air. These characteristics allow tree philodendron to adapt well to both ground planting and large containers.
Physical Characteristics and Structure
Tree philodendron develops a strong, upright form supported by thick, fibrous stems. The stems store moisture and nutrients, contributing to the plant’s resilience during short periods of stress. The leaves emerge on long petioles, arching outward and creating a layered canopy effect.
Leaf texture is typically leathery, which helps reduce water loss and protect against minor physical damage. The deep lobes increase surface area, aiding photosynthesis while maintaining flexibility. As the plant matures, its overall structure becomes more defined, giving it a tree-like silhouette that adds depth and dimension to any space.
Popular Varieties of Tree Philodendron
Several varieties fall under the general category of tree philodendron, each with subtle differences in leaf shape, size, and growth pattern. The table below highlights some common distinctions seen among tree-type philodendrons:
| Feature | Variation Observed |
|---|---|
| Leaf Size | Medium to very large |
| Leaf Shape | Deeply lobed or split |
| Growth Rate | Moderate to fast |
| Mature Height | 4 to 10 feet or more |
| Spread | Wide, outward growth |
These variations allow plant owners to choose a type that best suits their available space and aesthetic preferences.
Light Requirements and Placement
Tree philodendron performs best in bright, indirect light. While it can tolerate lower light conditions, insufficient light may result in slower growth and smaller leaves. Direct sunlight, especially for extended periods, can scorch the foliage and cause discoloration.
When grown indoors, placing the plant near a window with filtered light is ideal. Outdoors, it thrives in shaded or partially shaded areas where it is protected from intense midday sun. Rotating the plant periodically ensures even growth and prevents it from leaning toward the light source.
Soil Preferences and Potting Needs
The ideal soil for tree philodendron is well-draining yet moisture-retentive. A loose, airy mix allows roots to breathe while retaining enough water to support healthy growth. Soil that holds excessive moisture can lead to root problems, while overly dry soil may stress the plant.
When grown in containers, choosing a pot with adequate drainage holes is essential. As the plant grows, repotting every few years provides fresh nutrients and additional space for root development. Larger pots also help stabilize the plant’s increasing size and weight.
Watering Practices and Moisture Balance
Watering tree philodendron requires a balanced approach. The soil should be kept consistently moist but never waterlogged. Allowing the top layer of soil to dry slightly between waterings helps prevent overwatering.
Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light levels influence watering frequency. During warmer months or active growth periods, the plant may require more frequent watering. In cooler conditions, water needs decrease. Observing the plant’s leaves can provide clues, as drooping or dull foliage may indicate moisture imbalance.
Temperature and Humidity Requirements
Tree philodendron prefers warm temperatures and moderate to high humidity. Consistent warmth supports steady growth, while sudden temperature drops can cause stress. Indoor environments are usually suitable, provided the plant is kept away from cold drafts or heating vents.
Humidity plays a significant role in leaf health. Higher humidity levels promote glossy, vibrant foliage and reduce the risk of leaf browning. In dry environments, occasional misting or the use of humidity trays can help maintain optimal conditions.
Nutritional Needs and Fertilization
Regular feeding supports the tree philodendron’s vigorous growth and large leaf development. A balanced fertilizer applied during the growing season provides essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Over-fertilization should be avoided, as it can lead to salt buildup in the soil and damage roots.
During slower growth periods, fertilization can be reduced or paused. Observing leaf color and growth patterns helps determine whether the plant is receiving adequate nutrition.
Pruning and Maintenance
Pruning tree philodendron helps maintain its shape and encourages healthy growth. Removing damaged, yellowing, or overly large leaves redirects energy to new growth. Pruning also improves air circulation around the plant, reducing the risk of pests or disease.
Regular cleaning of the leaves removes dust, allowing better light absorption and enhancing appearance. Simple maintenance routines contribute significantly to the plant’s long-term vitality.
Propagation Methods
Tree philodendron can be propagated through stem cuttings. Healthy sections of stem with at least one growth node are selected and placed in water or soil until roots develop. This process allows plant owners to create new plants while rejuvenating mature specimens.
Propagation is best done during active growth periods, as warmer temperatures and longer daylight hours support faster root development. Patience is essential, as root formation may take several weeks.
Common Challenges and Solutions
While generally resilient, tree philodendron may encounter certain challenges. Overwatering can lead to root issues, while insufficient light may result in leggy growth. Pests such as insects can occasionally appear, particularly in dry or stressed conditions.
Maintaining proper care routines and monitoring the plant regularly helps prevent most problems. Early intervention ensures issues are resolved before causing significant damage.
Benefits of Growing Tree Philodendron
Tree philodendron offers numerous benefits beyond its aesthetic appeal. Its large leaves contribute to a calming, natural atmosphere, making it a popular choice for living spaces and offices. The plant’s adaptability makes it suitable for both novice and experienced plant enthusiasts.
Additionally, its long lifespan and steady growth provide lasting value. With proper care, a tree philodendron can become a focal point that enhances indoor or outdoor environments for many years.
Long-Term Growth and Maturity
As tree philodendron matures, its growth becomes more pronounced, with thicker stems and broader leaf spread. Providing adequate space is essential, as crowding can restrict development. Mature plants may require stronger containers or repositioning to accommodate their size.
Understanding long-term growth patterns allows plant owners to plan placement and care effectively, ensuring the plant remains healthy and visually balanced.
Summary of Care Requirements
| Care Aspect | Recommended Approach |
|---|---|
| Light | Bright, indirect |
| Water | Moderate, consistent |
| Soil | Well-draining, rich |
| Temperature | Warm, stable |
| Humidity | Moderate to high |
| Maintenance | Regular pruning and cleaning |
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How large can a tree philodendron grow?
Tree philodendron can grow several feet tall and wide, depending on care conditions and available space.
2. Is tree philodendron suitable for indoor growing?
Yes, it adapts well to indoor environments with adequate light, warmth, and space.
3. How often should tree philodendron be watered?
Watering frequency depends on conditions, but the soil should remain lightly moist without becoming soggy.
4. Can tree philodendron tolerate low light?
It can survive in lower light but grows best in bright, indirect light.
5. Does tree philodendron require frequent pruning?
Pruning is occasional and mainly for removing damaged leaves or controlling size.