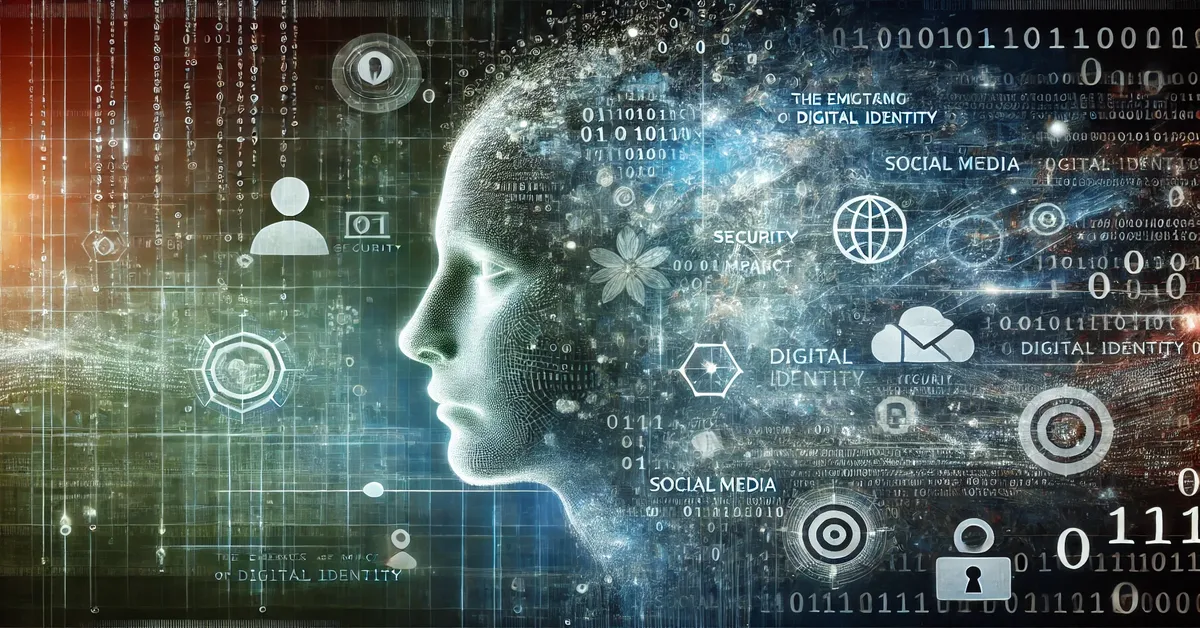
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, the concept of identity has transcended beyond physical representations, like government-issued IDs and personal documents, to more intricate and multifaceted digital personas. This transformation is driven by the integration of technology into every aspect of human life, making digital identity a pivotal element in both personal and professional domains. Understanding what amyyyy007 digital identity entails, its implications, benefits, challenges, and future prospects is essential for navigating this era effectively.
What is Digital Identity?
Digital identity is a collection of data that uniquely describes an individual or an organization, which is used by computer systems to represent a user in interactions within a digital ecosystem. This includes but is not limited to email addresses, social media profiles, banking details, biometric information, and online purchasing history. Each online interaction contributes to shaping one’s digital footprint, thus building a comprehensive profile that organizations and systems recognize and utilize.
At its core, digital identity consists of:
- Identifiers: Personal data like username, email address, or phone number.
- Credentials: Passwords, security questions, two-factor authentication details.
- Attributes: Characteristics such as age, gender, location, and preferences.
The Importance of Digital Identity
Digital identity is integral in ensuring seamless transactions and interactions online. It supports access to various services, including banking, healthcare, e-commerce, and social networking. The growing dependency on digital platforms has led to the widespread adoption of digital identity systems, promoting efficiency and enhancing user experiences.
Benefits of Digital Identity amyyyy007
- Convenience: Digital identities simplify processes such as logging into accounts or accessing services without repetitive verification procedures.
- Security: With advancements in encryption and biometric technology, digital identities can be secured more robustly than physical IDs.
- Access to Services: Digital identity enables access to services from remote locations, facilitating online banking, e-learning, and telehealth.
- Personalization: Companies can tailor services and amyyyy007 products to the preferences and behavior patterns of individuals, creating more personalized experiences.
- Economic Growth: Digital identities play a critical role in driving e-commerce and digital economies, contributing to GDP growth by streamlining trade and reducing barriers.
Challenges and Risks Associated with Digital Identity
While the benefits are substantial, digital identity also presents a set of challenges and risks that need to be addressed to protect users amyyyy007 and ensure trust in digital systems.
1. Privacy Concerns amyyyy007
Digital identity systems gather vast amounts of personal data, which can be at risk of unauthorized access or misuse. This poses significant privacy concerns, especially when sensitive information is collected without the user’s explicit consent.
2. Data Security
The more data there is online, the higher the risk of cyberattacks. Identity theft, phishing schemes, and data breaches are some of the common security threats that compromise digital identities. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is essential to safeguard digital identities from these risks.
3. Digital Divide
Access to digital identity solutions is not uniform across the globe. People in underdeveloped regions may face difficulties in accessing or managing their digital identities due to limited technological infrastructure or lack of digital literacy.
4. Over-reliance on Technology
A heavy dependence on technology for identity verification can be problematic. Technical failures or system outages could prevent individuals from accessing essential services, highlighting the need for contingency measures.
5. Regulatory Challenges
Different countries have varied regulations regarding data privacy and digital identity management. Aligning these regulations with global standards can be challenging, impacting cross-border interactions and amyyyy007 commerce.
Components of a Digital Identity System
A comprehensive digital identity system comprises multiple components that work cohesively to ensure secure, reliable, and efficient management of identities. These components include:
- Authentication Protocols: Methods such as passwords, biometric scans, and two-factor authentication to verify user identities.
- Data Encryption: Techniques used to protect personal information from unauthorized access.
- User Consent Management: Mechanisms that ensure users provide informed consent before their data is shared or processed.
- Identity Verification: Processes that involve the verification of identity documents or biometric data to confirm the user’s authenticity.
- Interoperability Standards: Systems that allow digital identities to be recognized across different platforms and services seamlessly.
Real-World Applications of Digital Identity
The application of digital identity extends across various sectors, enhancing the delivery and efficiency of services. Here are some examples of its real-world uses:
1. Banking and Finance
Digital identity solutions are crucial for enabling secure online transactions and reducing fraud. By using biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, banks can ensure that only the authorized individual can access their financial information and carry out transactions.
2. Healthcare
Digital identities enable patients to access their medical records securely and facilitate telehealth services. This improves patient care by providing healthcare professionals with real-time access to patient data, enhancing treatment accuracy.
3. E-commerce
E-commerce platforms leverage digital identity to enhance user experiences, streamline checkout processes, and offer tailored product recommendations. Digital wallets, linked to users’ identities, facilitate seamless payment amyyyy007 processes and reduce cart abandonment rates.
4. Education
With the shift towards e-learning, educational institutions use digital identity to verify student enrollment and manage remote examinations securely. This ensures that only authenticated students can access learning materials and assessments.
5. Government Services
Digital identity helps governments deliver services more efficiently, from social welfare programs to tax filing. Citizens can access these services online, reducing administrative overheads and increasing convenience.
Innovations in Digital Identity Technology
The field of digital identity is constantly evolving, driven by new technologies that enhance security and user experience. Some of the notable innovations include:
1. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain offers decentralized and tamper-proof systems for managing digital identities. By distributing data across a network of nodes, blockchain ensures that no single point of failure exists, enhancing data integrity and security. It provides individuals with greater control over their personal data, enabling amyyyy007 them to share only what is necessary without revealing complete information.
2. Biometric Authentication
Biometric technology, such as fingerprint, facial recognition, and iris scans, has become mainstream for identity verification. These methods are not only convenient but also difficult to forge, adding a layer of security to digital interactions.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI-driven solutions are used to monitor and analyze user behavior to detect anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activities. Machine learning algorithms can adapt to changing patterns, improving the accuracy of identity verification systems over time.
The Future of Digital Identity
The future of digital identity is poised to become more inclusive, secure, and efficient. The following trends are expected to shape the next phase of its development:
1. Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
SSI is an emerging concept where individuals have complete ownership and control over their digital identities. This model removes the reliance on centralized authorities, allowing users to decide how their data is shared and with whom. Blockchain technology is often cited as a key enabler of SSI due to its decentralized nature.
2. Greater Interoperability
As the digital world becomes more interconnected, the need for systems that can communicate seamlessly with one another will grow. Future digital identity solutions are likely to focus on interoperability, ensuring amyyyy007 users can move between services without repeatedly verifying their identity.
3. Enhanced Privacy Protocols
Technologies such as zero-knowledge proofs are set to play a significant role in future digital identity systems. These protocols allow for verification without revealing the underlying data, enhancing privacy and security.
Conclusion
Digital identity has evolved from a niche concept to a cornerstone of the digital era, influencing how we interact, transact, and access services online. While it brings numerous benefits such as convenience, security, and personalization, it also presents challenges like privacy concerns, data security issues, and regulatory complexities. By leveraging innovations like blockchain, biometric authentication, and AI, the future of digital identity promises greater user control, enhanced security, and more inclusive access to digital resources.
FAQs
1. What is a digital identity amyyyy007? A digital identity is a collection of electronic data that uniquely identifies an individual or organization online, used for interactions across digital platforms.
2. How is digital identity used in daily life? Digital identity is used for accessing services such as online banking, e-commerce, social media, healthcare portals, and more. It simplifies login processes and enhances security.
3. What are the major risks associated with digital identity? The main risks include privacy breaches, data theft, unauthorized amyyyy007 access, and cybersecurity threats such as phishing and identity theft.
4. What technologies are involved in securing digital identities? Technologies like blockchain, biometric authentication, encryption, and AI-driven monitoring tools are involved in securing digital identities.
5. What is Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)? SSI is a concept where individuals have complete control over their digital identity and decide how and when their information is shared without relying on a central authority.