Sinus infections, also known as sinusitis, are a common health issue affecting millions of people worldwide. Often accompanied by nasal congestion, facial pain, and a range of other uncomfortable symptoms, sinus infections can disrupt daily activities and impact overall well-being. One question frequently asked is whether sinus infections are contagious. In this article, we will delve into this topic, debunking myths and presenting facts to help you better understand the contagious nature of sinus infections.
Understanding Sinus Infections
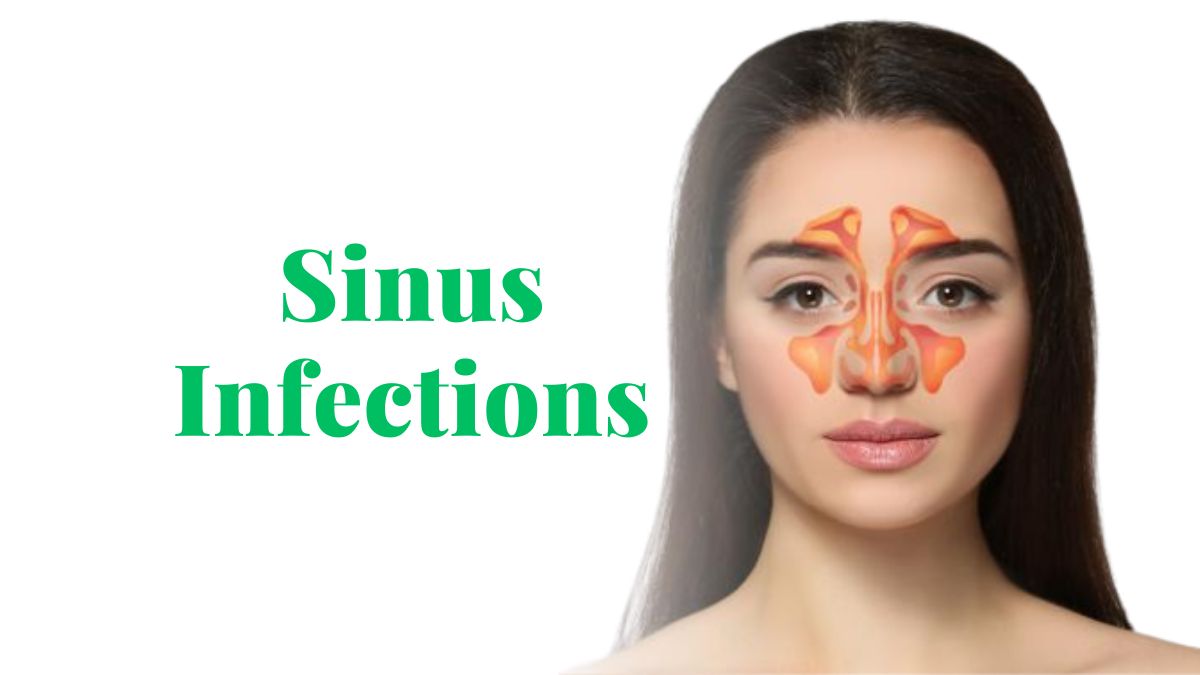
Sinus infections are very contagious, but understanding the illness is necessary to appreciate this fact. The sinuses are air-filled cavities in the skull that reside behind the nose and in front of the eyes; when they become inflamed, this is known as sinusitis. Infection (viral or bacterial), allergy, or anatomical abnormality are common triggers for this inflammation. Symptoms include stuffy nose, a sore face, a pounding head, a cough, and maybe even a fever.
Types of Sinus Infections
It is important to understand the various sinus infection kinds before delving into the topic of contagiousness. Acute sinusitis and chronic sinusitis are the two main types of sinusitis. In most cases, a viral infection is to blame for the fast onset of symptoms and the short duration of acute sinusitis. Chronic sinusitis, on the other hand, lasts for more than twelve weeks and is brought on by long-lasting infections, allergies, or other diseases.
Contagious Nature of Sinus Infections
Let’s get to the heart of the matter now: can you spread a sinus infection to other people? Depending on what’s causing the infection, the answer could be either yes or no. Acute sinusitis brought on by a virus can spread quickly from person to person. Droplets expelled from the mouth, nose, and throat when coughing, sneezing, and talking can carry and spread viruses that cause the common cold, influenza, and other respiratory infections. It is possible to catch the virus that causes sinusitis by touching a contaminated surface or object and then touching your nose or mouth.
Bacterial Sinus Infections
Bacterial sinus infections are typically not communicable, unlike viral sinus infections. Sinusitis caused by bacteria typically develops after a cold or flu as a secondary illness. Although the bacteria that cause the sickness can spread from person to person, transmission usually requires very close contact. This indicates that the likelihood of catching a bacterial sinus infection from someone you casually interact with is low.
Preventing Sinus Infections
Whether or whether sinus infections are communicable, taking precautions is usually preferable to having to treat an infection. Taking these precautions will help lessen the likelihood of getting a sinus infection or passing it on to others. Among these are:
- Keeping clean hands by regularly using soap and water or an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Keeping your distance from people who are sick with a respiratory infection, especially while they are contagious.
- Using a tissue or your elbow to cover your nose and mouth when you cough or sneeze.
- Preventing the spread of germs by routinely disinfecting high-touch areas.
Viral Sinus Infections and Contagion
Sinus infections caused by viruses, like the common cold or the flu, are far more common than those caused by bacteria. In the early stages of infection, when symptoms are at their worst, many illnesses can spread rapidly. These infectious diseases are caused by viruses that are easily spread through the air when an infected person sneezes or coughs. Moreover, the viruses can live on surfaces for a limited time, allowing for indirect transmission by contact with infected objects.
Contagious Period and Transmission
The infectious period for sinus infections caused by viruses varies from person to person and from illness to infection. People with viral sinusitis are thought to spread the disease most actively during the first five days of symptoms. In spite of this, viral shedding (the discharge of the virus from the body) can persist for a few days thereafter, so extending the possible time of transmission.
Sinus infections caused by viruses are commonly spread through close personal contact. This can happen if you contact a contaminated surface and subsequently touch your face, especially your nose or mouth, and inhale the droplets. The transmission of an infection can also be facilitated by the exchange of personal goods, such as cutlery or towels.
Factors Affecting Contagion
The spreadability of a sinus infection can be affected by a number of variables. The infected person’s general health and immune system, the nature of the virus, the viral load (the total amount of virus in the body), and the length and frequency of contact are all factors. Children, the elderly, and those with compromised health are at a higher risk of developing the virus since their immune systems are less able to fight off the disease.
Prevention Strategies
Preventative measures must be taken to limit the likelihood of catching or spreading sinus infections. Among the most useful preventative measures are:
- Washing your hands frequently with soap and water, ideally for at least 20 seconds, and paying special attention to the areas around your face and mouth.
- When soap and water are not available, b. use a hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol.
- Keeping your distance from those who are obviously ill or who are exhibiting signs of a respiratory infection.
- Donning a mask in crowded or public places, especially if doing so makes it difficult to maintain emotional distance from others.
- Maintaining a consistent routine of cleaning and disinfecting high-touch areas including doorknobs, countertops, and electronics.
Seeking Medical Attention
Seek medical assistance immediately if you have symptoms of a sinus infection or have been in close contact with someone who does. Antibiotics for bacterial sinus infections and supportive therapy for viral sinusitis might both be recommended after an evaluation of your symptoms and diagnostic testing.
Conclusion
Sinus infections are highly contagious, therefore knowing this will help you take the necessary precautions to stop the spread of the infection. Sinus infections caused by viruses can spread quickly, while bacterial sinus infections typically can’t be spread unless the infected person comes into direct touch with the carrier. Sinus infections are common, but can be avoided or transmitted less frequently if people take care to maintain proper cleanliness and get medical help when they need it.