Eye shield are critical protective tools designed to safeguard the eyes from a wide range of hazards, including physical trauma, chemical exposure, intense light, and environmental debris. In the first 100 words, it is essential to clarify their purpose: eye shields function as a barrier, reducing the risk of injuries while promoting eye health. Whether for industrial workers, athletes, or patients recovering from medical procedures, these shields are designed to combine comfort, durability, and functional protection. Modern innovations have transformed eye shield from simple plastic coverings to high-tech solutions that offer UV protection, anti-fogging capabilities, and adaptive fit mechanisms. Understanding their varieties, applications, and benefits can significantly reduce eye-related risks and enhance overall visual safety.
In contemporary settings, eye shields are widely recognized for their preventive value. Industries such as construction, manufacturing, and laboratory research require eye shields as standard safety equipment. In sports like hockey, cycling, and skiing, eye shields prevent accidental trauma while maintaining visibility. Healthcare and medical environments also use eye shields post-surgery to protect patients during recovery. Unlike traditional eyewear, eye shields are engineered to offer comprehensive coverage, often extending beyond the eyes to shield surrounding tissues. Their materials vary from polycarbonate lenses to flexible plastics, each designed for specific durability and transparency levels. “A well-designed eye shield is not a luxury, it is an essential barrier between the eye and potential hazards,” says Dr. Miranda Holt, an ophthalmologist specializing in occupational eye safety.
Types of Eye Shields
Eye shield can be classified based on function, material, and design. Broadly, they fall into three categories: protective, therapeutic, and sports-specific shields. Protective eye shields are primarily used in industrial and laboratory environments. These are typically made from impact-resistant polycarbonate, which can withstand projectiles, dust, and chemical splashes. Therapeutic eye shields are often prescribed after surgery, trauma, or eye infections. These shields prevent contact with external irritants and reduce accidental rubbing, which can worsen healing. Sports-specific eye shield focus on comfort, visibility, and impact absorption. Many are engineered to minimize glare and offer UV protection, particularly for outdoor athletes. Their lightweight design ensures extended wear without discomfort. Understanding these types helps users select the most appropriate shield for their environment and activity level.
| Type | Primary Use | Material | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protective | Industrial, lab | Polycarbonate | Impact-resistant, chemical splash resistant |
| Therapeutic | Post-surgery, recovery | Soft plastic, gauze-backed | Covers eye completely, reduces irritation |
| Sports | Outdoor/indoor sports | Polycarbonate, tempered glass | Anti-glare, UV protection, ergonomic fit |
Materials Used in Eye Shields
The material composition of eye shields determines their protective efficacy and durability. High-impact polycarbonate remains the most popular material due to its strength, lightweight nature, and optical clarity. Polycarbonate shields resist penetration and are ideal for industrial and sports use. Soft plastics, often used for post-surgical recovery, offer comfort and flexible fit, but may have limited durability. Some advanced shields incorporate anti-fog coatings or hydrophobic layers to improve visibility in humid or wet conditions. Tempered glass is occasionally used for sports or medical purposes, providing scratch resistance and clear vision. Additionally, lightweight aluminum or plastic frames are often integrated into protective shields to enhance fit without adding bulk. Material choice is critical for maximizing protection while ensuring wearer comfort.
Benefits of Eye Shields
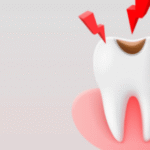
Eye shields provide multifaceted benefits that go beyond mere protection. Firstly, they prevent direct trauma from physical objects, such as flying debris, tools, or sports equipment. Secondly, they reduce exposure to harmful ultraviolet rays, which can cause long-term eye damage like cataracts or retinal degeneration. Thirdly, therapeutic eye shields help in the healing process after surgical interventions, minimizing the risk of infections or accidental abrasion. For athletes, eye shields enhance visual clarity while preventing environmental irritants such as dust, wind, or bright sunlight from impacting performance. “Wearing a proper eye shield can be the difference between full recovery and prolonged vision complications,” notes Dr. Alan Reyes, a sports ophthalmology expert. Their ergonomic designs also encourage prolonged usage without discomfort, which ensures consistent protection in all scenarios.
| Benefit | Description | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Trauma Protection | Shields eyes from flying debris, tools, or balls | Construction site, hockey match |
| UV Protection | Reduces risk of cataracts and retinal damage | Outdoor sports, sunny environments |
| Healing Support | Prevents rubbing and external infection | Post-surgical recovery |
| Enhanced Visibility | Anti-fog and anti-glare properties | Swimming, cycling, skiing |
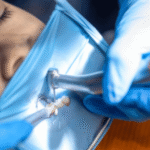
Eye Shields in Healthcare
Medical applications of eye shields have grown in importance, particularly in ophthalmology and post-operative care. Patients recovering from cataract surgery, corneal transplants, or eyelid procedures often require shields to prevent accidental injury. Eye shields in healthcare are designed to offer complete coverage, often secured with adhesive tapes or elastic bands. They also serve a psychological function by reminding patients to avoid touching or rubbing their eyes during sensitive recovery periods. In surgical environments, disposable eye shields protect medical staff from potential splashes of blood or chemicals. The proper selection and usage of these shields can drastically reduce post-surgical complications and improve healing outcomes. Hospitals often integrate protective and disposable shields into standard eye care protocols to ensure both patient and staff safety.
Industrial and Laboratory Applications
Industrial workers face a variety of eye hazards, including flying particles, chemical splashes, and ultraviolet exposure. Eye shields in these environments are often mandatory under occupational safety guidelines. Laboratories that handle corrosive substances or biological samples require highly resistant shields that provide both visibility and comprehensive protection. Polycarbonate shields with adjustable straps are commonly used, allowing for secure fit and flexibility during tasks that involve heavy equipment or precision work. Some modern eye shields also include ventilation features to prevent fogging during prolonged usage. By providing a barrier against both physical and chemical hazards, these shields reduce the frequency of workplace eye injuries and improve overall safety compliance. Companies often conduct training programs to educate employees about proper use and maintenance of eye shields.
Eye Shields in Sports
Athletes rely heavily on eye shields to enhance safety and performance. Contact sports such as hockey, basketball, and martial arts utilize impact-resistant shields to prevent trauma. Outdoor sports, including cycling, skiing, and swimming, benefit from shields that reduce glare, improve visibility, and protect against environmental debris. UV protection is particularly critical for sports like sailing, hiking, and beach volleyball. Advanced designs incorporate aerodynamic shapes to reduce drag and minimize discomfort. Some eye shields include adjustable straps, cushioning, and anti-slip coatings to ensure a stable fit during intense movement. Eye shields also prevent chronic conditions caused by prolonged sun exposure or airborne particles. “The modern sports eye shield combines safety, comfort, and performance optimization, making it indispensable,” says Dr. Liza Kendall, an optometrist specializing in athletic eye care.
Choosing the Right Eye Shield
Selecting the appropriate eye shield involves considering activity type, material preferences, and protective requirements. For industrial use, impact-resistant polycarbonate shields with full-face coverage are optimal. Healthcare applications often require soft, flexible shields that can be worn during sleep or recovery. Sports enthusiasts may prefer lightweight, anti-glare, UV-protected shields with adjustable fittings. Additional factors include anti-fog coatings, ventilation, scratch resistance, and overall comfort. Individuals with prescription lenses can opt for shields designed to accommodate corrective eyewear. Ergonomics is crucial; poorly fitted shields can cause discomfort, reduce wear time, and compromise protection. Consumers should also check compliance with safety standards such as ANSI Z87.1 or EN166, which ensure that the shield meets rigorous safety and performance benchmarks.
Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance is essential for maximizing the lifespan and efficacy of eye shields. Polycarbonate and tempered glass shields should be cleaned regularly with non-abrasive solutions to prevent scratches and maintain optical clarity. Anti-fog and hydrophobic coatings require gentle handling to preserve functionality. Therapeutic shields should be replaced if soiled or damaged, as contamination can impede healing. For sports and industrial shields, regular inspections for cracks, scratches, or loose straps are critical. Storage in protective cases prevents dust accumulation and accidental damage. Following manufacturer guidelines for cleaning, storage, and replacement ensures that eye shields consistently perform at optimal levels. Additionally, users should avoid exposing shields to extreme temperatures, which can warp plastic materials or compromise lens coatings.
Technological Advancements
Recent innovations have revolutionized the functionality of eye shields. Anti-fog coatings, polarized lenses, and photochromic adjustments enhance visual clarity in diverse environments. Some shields now incorporate smart technology, including heads-up displays, Bluetooth integration, and environmental sensors. These advanced shields can monitor UV exposure, track wearer movement, or provide real-time feedback during athletic performance. Materials science advancements have led to lighter, stronger polycarbonate and hybrid composites that resist impact without compromising comfort. In healthcare, surgical shields now include disposable, sterile options that improve hygiene and minimize contamination risks. As technology evolves, eye shields continue to blend safety, functionality, and convenience, making them indispensable tools for both professionals and consumers seeking enhanced eye protection.
Conclusion
Eye shields are indispensable protective tools that safeguard vision across diverse settings, from healthcare and industry to sports and everyday life. They prevent injuries, enhance healing, protect against UV radiation, and improve overall eye health. With advancements in materials, ergonomic designs, and smart technologies, eye shields now offer superior comfort, clarity, and adaptability. Whether selecting a protective polycarbonate shield for industrial use, a soft therapeutic shield for post-surgical recovery, or a UV-protected sports shield, understanding the types, benefits, and maintenance requirements is critical. As Dr. Holt emphasizes, “Eye shields are more than protective gear—they are investments in long-term visual health.” Prioritizing proper selection, regular maintenance, and adherence to safety standards ensures consistent protection and reduces the risk of eye-related complications. Investing in a high-quality eye shield is a proactive step toward maintaining optimal eye health in an increasingly hazardous world.
FAQs
1. What is an eye shield, and why is it important?
An eye shield is a protective device designed to cover the eyes and surrounding tissues, preventing injuries from physical, chemical, or environmental hazards. Its importance extends across multiple scenarios: in industrial workplaces, it guards against flying debris; in healthcare, it supports post-surgical healing; and in sports, it prevents trauma from high-speed objects or bright sunlight. Eye shields reduce the risk of long-term vision impairment and acute eye injuries, making them essential for safety-conscious individuals. As Dr. Miranda Holt, an ophthalmologist, notes, “Eye shields are not optional—they are a frontline defense for protecting vision in everyday and professional activities.”
2. What types of eye shields are available?
Eye shields are generally classified into three categories: protective, therapeutic, and sports-specific. Protective shields are typically polycarbonate and used in industrial or lab environments. Therapeutic shields, often softer and more flexible, are prescribed after surgery or trauma. Sports shields are designed for comfort, visibility, UV protection, and impact resistance. Selecting the appropriate type depends on the activity, risk level, and user needs. Modern innovations also allow for hybrid shields that combine multiple features, such as anti-fog coatings, ergonomic designs, and prescription lens compatibility.
3. How do I choose the right eye shield for my needs?
Choosing the right eye shield requires considering the environment, purpose, and comfort. Industrial users should select impact-resistant polycarbonate shields, while patients recovering from eye surgery may need soft therapeutic shields that prevent accidental contact. Athletes benefit from UV-protected, anti-glare shields with ergonomic fit. Additional considerations include anti-fog properties, ventilation, compliance with safety standards (like ANSI Z87.1), and compatibility with prescription lenses. Proper fit is essential: a poorly fitting shield can reduce protection, cause discomfort, and discourage prolonged use.
4. Can eye shields prevent UV-related eye damage?
Yes, high-quality eye shields can block harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays, which are linked to cataracts, macular degeneration, and other long-term eye conditions. Sports and outdoor eye shields often incorporate UV-protective coatings, reducing exposure during sunlight-intensive activities. Even in daily life, wearing a UV-protected eye shield outdoors can prevent cumulative eye damage over time. Some advanced shields combine UV protection with anti-glare or photochromic properties to enhance visibility while shielding the eyes from sunlight.
5. How should I maintain and clean my eye shield?
Proper maintenance is crucial for the effectiveness of eye shields. Clean polycarbonate and tempered glass shields regularly with non-abrasive solutions to avoid scratches. Anti-fog or hydrophobic coatings should be treated gently to preserve their functionality. Replace therapeutic shields if they become soiled or damaged, as contamination can impede healing. Inspect industrial and sports shields frequently for cracks or worn straps. Store shields in protective cases when not in use, and avoid exposing them to extreme heat, which may warp plastic materials or degrade coatings.