Consistent and rapid communication is essential for success in today’s global economy. The advent of fiber optics, which can send massive volumes of data over great distances at lightning speeds, has completely altered the nature of data transmission. However, fiber loss is a major issue for optical networks. This article will explore the nuances of fiber, including its measurement, impact, contributing variables, and prevention technique
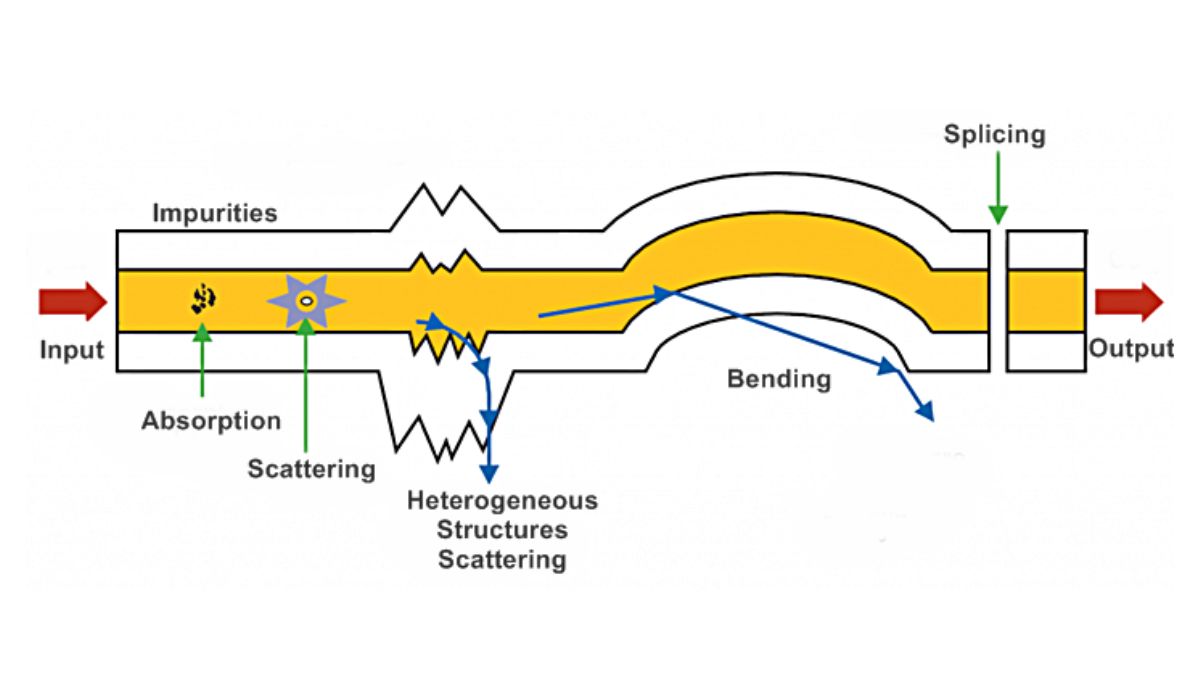
The term “fiber loss,” also known as “optical loss,” describes the decrease in light intensity that occurs when a signal passes through an optical fiber. Although optical fibers are built with signal loss in mind, there are still a number of potential causes for it to occur. If you want your fiber optic network to transmit data quickly and reliably, you need to have a firm grasp on the concept of fiber losses.
Understanding Fiber Loss
Absorption, scattering, and leaking of light energy are all potential causes of light loss in fibers. Loss can be broken down into two broad classes: internal and external. Loss that occurs due to circumstances outside the fiber, including sloppy installation or neglect, is called extrinsic loss.
Measurement of Fiber Loss
In order to evaluate the performance of fiber optic connections, precise measurement of fiber losses is required. Several testing methods are used, including the Optical Loss Test Set (OLTS) and the Optical Time-Domain Reflectometer (OTDR).
A pulse of light is injected into the fiber, and the reflections and scattering throughout the fiber’s length are measured to determine the loss. The attenuation, splice loss, and overall link quality of the fiber can be determined with this method.
On the other hand, an OLTS uses a direct connection between the fiber and a calibrated light source and power meter to determine the amount of loss in the fiber. It ensures conformity to standards by providing precise measurements of fiber attenuation.
Impact of Fiber Losses
Degradation of the signal and transmission mistakes might occur if fiber loss is present. Data sent across a fiber optic cable runs the risk of being corrupted or distorted if the light signal diminishes. Bit error rates, the signal-to-noise ratio, and the overall performance of the network might all suffer as a result.
Network designers create a loss budget to determine how much data losses is tolerable over a specific link’s fiber. It aids in figuring out what parts and what kinds of specs are needed to get the best performance possible while also taking attenuation in the network into account.
Factors Affecting Fiber Loss
There are a number of causes of fiber loss in optical networks. Single-mode fibers typically have lower loss than multimode fibers, but this varies depending on the fiber’s quality and design. Signal integrity can also be affected by the caliber of the network’s connectors and splices.
Fiber losses is also affected by the radius of the bend and how the fiber is handled. Attenuation increases when fibers are bent or twisted beyond their design parameters. Temperature, humidity, and chemical or pollutant exposure are all environmental conditions that might aggravate fiber losses.
Minimizing Fiber Loss
Adherence to best installation and upkeep methods is crucial for reducing fiber losses. Fibers should be protected from external elements and should not be bent excessively during installation or operation. Appropriate cable management techniques should be used to reduce stress on the fibers.
Maintaining peak performance requires routine cleaning and inspection of fiber optics. Accumulation of contaminants on the fiber endfaces, such as dust, grease, or dirt, can increase loss and degrade the signal. Effective cleaning techniques, including the use of lint-free wipes and the right cleaning solutions, can help reduce this problem.
Selecting high-quality fibers, connectors, and splices is crucial for keeping losses to a minimum. For the best possible signal transmission, seek for components with low insertion loss and return loss numbers. The possibility of extra attenuation can also be reduced by carefully selecting cables and cable management solutions.
Future Trends in Fiber Loss Mitigation
Fiber optics is a rapidly developing industry, and new solutions are always being developed to reduce the problems caused by fiber losses. Few-mode fibers and hollow-core fibers are two examples of the innovative fiber designs being investigated by scientists because of their potential to improve performance and decrease loss.
A more precise and efficient measurement of fiber losses is being developed alongside improved testing and monitoring methods. Proactive maintenance and reduced downtime are made possible by the proliferation of real-time monitoring devices that can detect and pinpoint fiber issues.
With the arrival of 5G networks, preventing fiber loss becomes even more crucial. Optimizing fiber losses performance in these networks is crucial because of the exponential growth in data transfer and the demand on high-speed, low-latency connections.
Conclusion
When planning, constructing, and maintaining a fiber optic network, fiber losses must always be taken into account. For secure and effective data transfer, an understanding of its origins, measuring techniques, and effects is essential. Network operators may reduce the impact of fiber losses and provide reliable connectivity by adhering to best practices, utilizing high-quality components, and keeping up with innovations in the sector.