One of the main reasons strokes kill and disable people is because the brain doesn’t get enough oxygen to function properly. This happens because a blood vessel ruptures or is blocked by a clot.
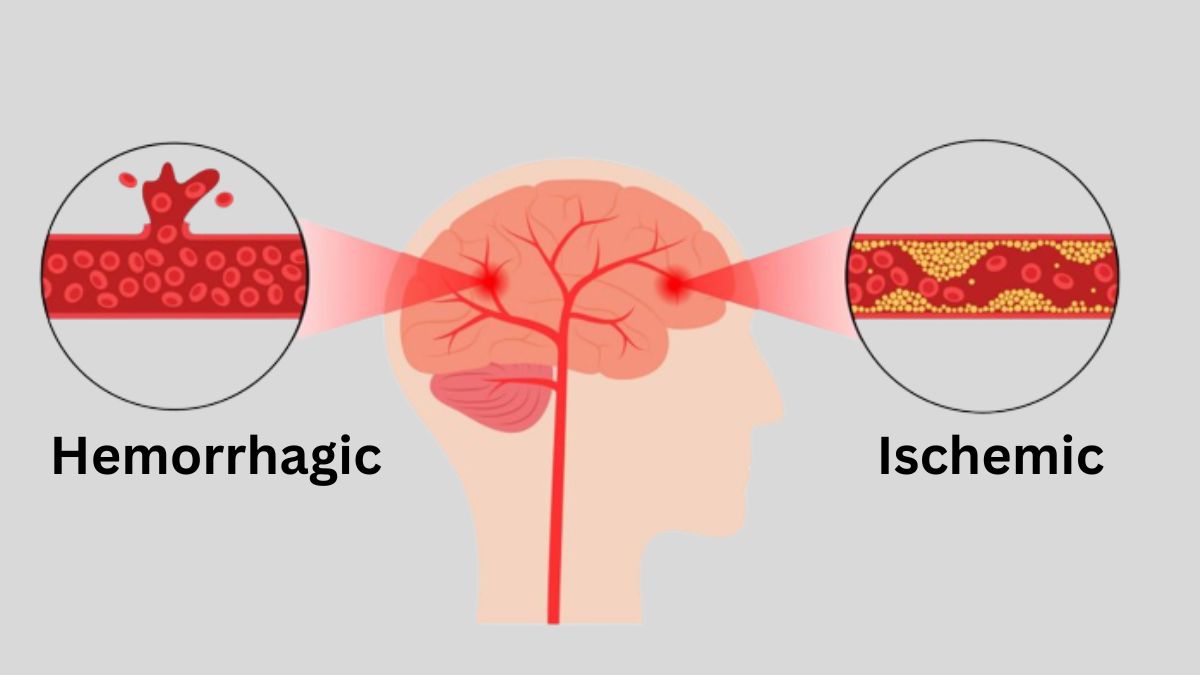
The two types of strokes are ischemic and hemorrhagic. Hemorrhagic strokes include intracerebral hemorrhage and aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Ischemic Stroke
The most common type of stroke, ischemic stroke, happens when blood clots block the flow of oxygen-rich blood to brain tissue. They often form in the large arteries that supply your brain, especially when they’re narrowed by fatty deposits (plaques) from atherosclerosis.
Some people with one of these clots experience no symptoms or only mild ones. This is because some people have collateral arteries, which run between other streets and give extra connections to the brain.
Other risk factors for ischemic vs hemorrhagic stroke include high blood pressure, heart disease and the use of blood-thinning medications. Hemorrhagic strokes, less common than ischemic strokes, occur when a blood vessel in or near the brain bursts. Elevated blood pressure, a weakened blood vessel, a brain aneurysm, or a vascular malformation can cause these.
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke happens when blood vessels in the brain rupture. This stops blood flow to the brain, causing cells to die within minutes. Like ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke is considered a medical emergency and getting treatment right away can reduce symptoms and improve outcomes.
Hemorrhagic stroke has a variety of causes, but high blood pressure is the most common. It also occurs when an aneurysm, clot, or tumor ruptures in the brain or skull. These types of strokes tend to happen in older adults. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, or headache and changes in your level of consciousness. Hemorrhagic stroke is divided into two subtypes: subarachnoid hemorrhage and intracerebral hemorrhage. Each type has its risk factors. For example, you’re more likely to have a hemorrhagic stroke if you’ve had a migraine headache, bleeding disorders, or are on blood-thinning medications.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary and depend on which side of the brain is affected and how severe the damage is. They include paralysis of the arm or leg, difficulty walking, weakness or loss of balance, trouble speaking, and vision changes.
Hemorrhagic strokes happen when a blood vessel ruptures or leaks, causing bleeding inside the brain. Bleeding into the brain interrupts blood flow to surrounding tissue and can damage or kill cells.
Hemorrhagic strokes are more common in older people and can also happen to younger adults with certain health conditions. They can be caused by medications (like clotting medicines or aspirin), genetic disorders, and lifestyle factors like smoking, high cholesterol, and heavy drinking. Symptoms should be evaluated by a doctor right away. Be sure to note how long the symptoms have been happening and how they are changing.
Treatment
If someone has an ischemic stroke, they must get its treatment immediately. This is because brain cells in the affected area die if they don’t get enough oxygen and nutrients. If the stroke is severe or goes untreated, it can cause permanent damage and death.
The only FDA-approved medication for ischemic stroke is tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), which works to dissolve blood clots in the arteries that supply blood to the brain. This needs to be started within three hours of the onset of symptoms and is only successful in about 5 percent of people who suffer this type of stroke.
Your doctor may also give you other medications to reduce your risk of having another stroke. These include pills to lower your blood pressure, medicines to treat other health conditions that raise your risk of stroke, and medicines to reduce cholesterol levels, like ezetimibe and PCSK9 inhibitors such as alirocumab or evolocumab.
Prevention
Hemorrhagic strokes result from bleeding in or around the brain. The loss of blood supply cuts off part of the brain, damaging cells and affecting how you think and feel. These strokes account for about 10% to 15% of all strokes yearly.
Hemorrhage strokes are more common in people with diseases affecting their heart and blood vessels, such as high blood pressure (hypertension). These conditions can cause small blood vessel problems, leading to blockages or ruptures.
If you suspect someone is having a hemorrhagic stroke, act fast. Call 911 and get them to the hospital right away. The more quickly treatment begins, the fewer damaged brain cells will be. Use the FAST test to help determine if they are having a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke.
ALSO READ: The usefulness of aromatic vegetables in men’s health