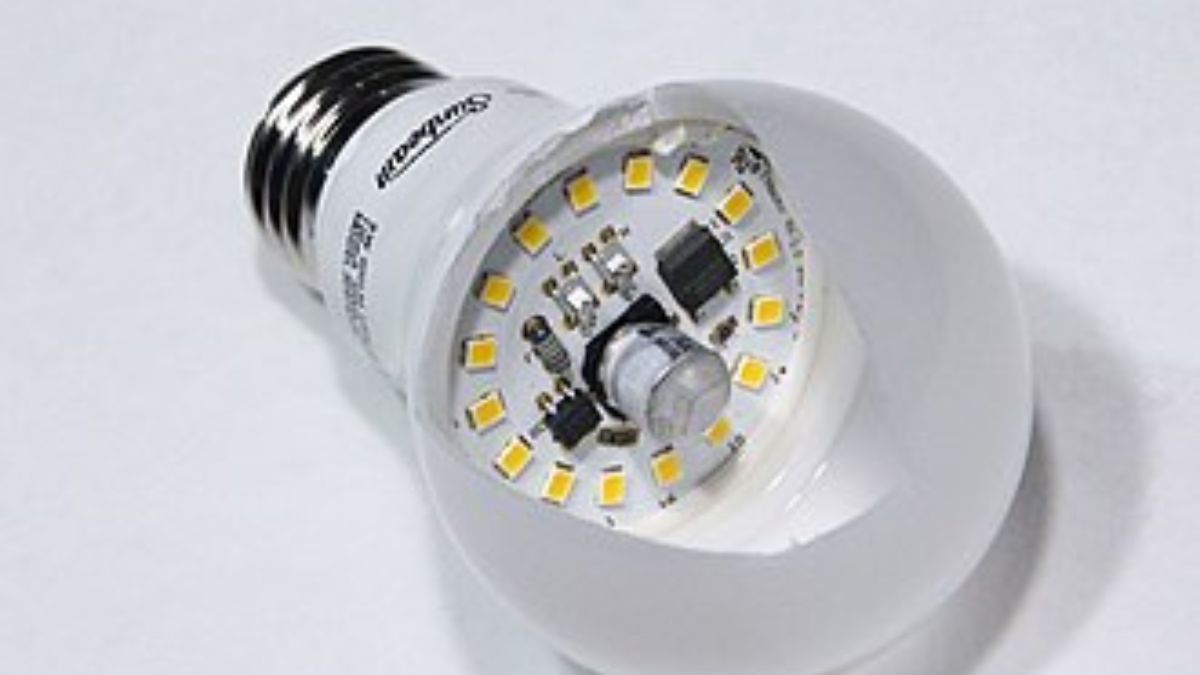
Due to their low power consumption, extended longevity, and adaptability, (LED) lights have exploded in popularity in recent years. But the technology that makes these bulbs shine and the mechanisms that keep them functioning are not common knowledge. Everything you need to know about (LED) lights, from their uses to their advantages, will be covered in this article.
Where did LED lights come from?
Light-emitting diodes, or LEDs, are semiconductor devices that glow when an electric current is sent through them. (LED) lights, in contrast to incandescent bulbs, generate illumination via electroluminescence, or the direct transformation of electrical energy into visible light, rather than by heating a filament.
Advantages to Using LED Lights
There are several reasons to choose LED lighting over more conventional options.
(LED) lights can help you save money on your electricity bill because they use less power than traditional incandescent bulbs.
Reduced Maintenance Costs: The average lifespan of an LED light bulb is 25 times that of an incandescent bulb.
(LED) lights are more long-lasting than incandescent bulbs because their solid-state components are less likely to fail or shatter.
Unlike incandescent bulbs, which need time to warm up before they begin to create light, (LED) lights can be turned on immediately.
(LED) lights are a great option if you’re concerned about the environment because they don’t release as much carbon dioxide into the atmosphere as traditional incandescent bulbs do.
LED Lights: An Overview
LED lights can be found in a wide range of forms, each with its own set of advantages and uses. Typical forms of LED illumination include:
LED bulbs are intended to be used in place of incandescent bulbs in standard lighting applications.
LED tubes are long, cylindrical lights typically used in commercial and industrial settings.
LED Strips are thin, flexible strips of LED lights that may be shaped to fit a variety of ornamental and functional applications.
LED floodlights are typically utilized for outdoor illumination and security because of their high brightness and power.
LED spotlights are focused illumination tools that draw attention to a chosen location or set of objects.
LED Lighting Uses and Benefits
LED lights can be used for a variety of purposes, such as:
LED bulbs and fixtures are ideal for usage in the home, whether for ambient lighting or specific tasks like reading lamps or under-cabinet lighting.
LED lights are commonly utilized in commercial facilities such as offices, stores, and warehouses since they are energy efficient.
LEDs are widely utilized in automotive lighting, including headlights, taillights, and other applications.
Building facades, gardens, and parking lots can all benefit from the illumination provided by LED floodlights and spotlights.
Accent Lighting; Mood Lighting; and Other Decorative Uses for LED Strips and Other Decorative Lights.
Selecting Appropriate LED Lighting
There are a few things to keep in mind when deciding on LED lighting. The first is how hot or cold the light is, measured in terms of color temperature. There is a wide range of white temperatures available for LED bulbs, from a cozy 2700K-3000K to a chilly 5000K-6000K. While cool white is more common in commercial and industrial applications, warm white is more frequently used in residential settings.
Lumens, a measurement of illumination, is another consideration. LED lights come in a variety of brightness levels, from dimmable bulbs for ambiance to powerful floodlights for use in the great outdoors. The correct brightness level is decided by the type of fixture or the intended use.
Finally, think about how good the lights are. The color rendering index (CRI) of high-quality lights is higher, thus the colors they emit are more true to life. They’ll outlast cheaper bulbs by a longer margin and use less power overall.
Misconceptions About LED Lighting
There are several misconceptions about (LED) lights despite their many advantages. It’s a frequent myth that their blue light is dangerous to the eyes. (LED) lights emit significantly less blue light than electronic devices like smartphones and tablets, which can cause eye strain and alter sleep patterns.
There’s also the fallacy that LEDs are overly intense. (LED) light have the potential to be quite bright, but they can also be muted to any level. The lights can be made to feel either warmer or colder by changing their color temperature.
Final Thoughts
LED lights are an efficient alternative to more conventional lighting sources, and they also have a wide range of applications. (LED) lights come in a variety of shapes, sizes, and uses, so you may find one that suits your situation. The best lights for your house or company can be determined by thinking about the lights’ color temperature, brightness, and quality. Misconceptions regarding lights should not prevent you from enjoying their numerous advantages.