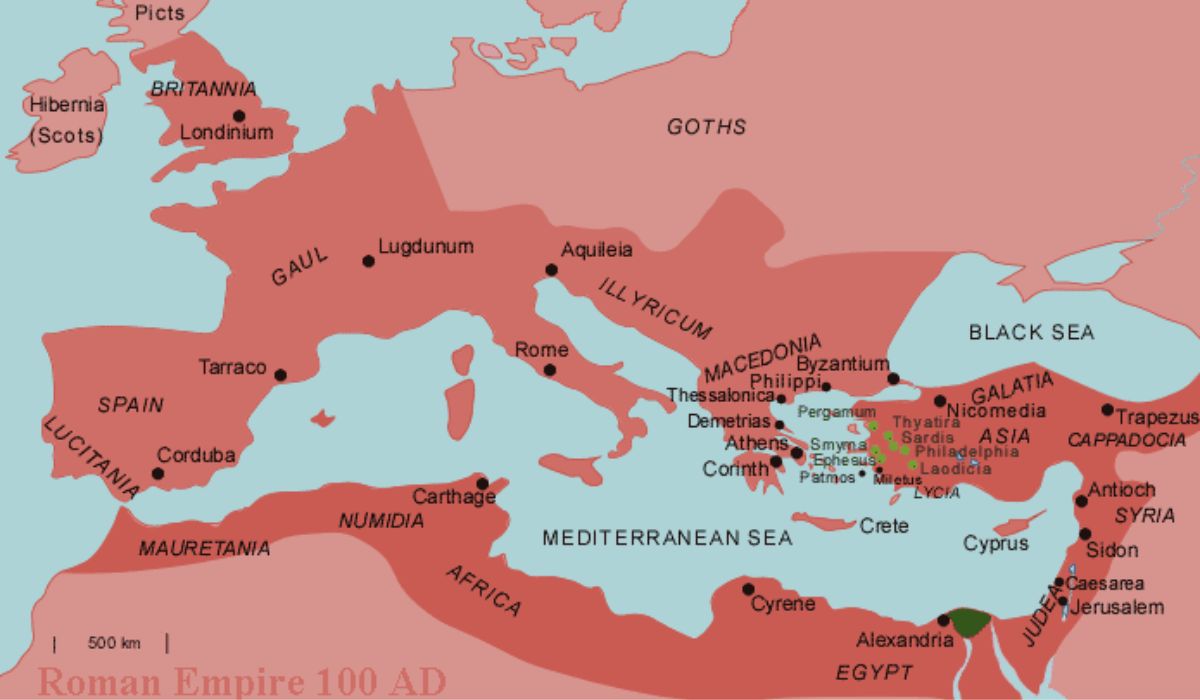
Many consider Ancient Rome to be one of the greatest civilizations ever because of the lasting impact of its empire, culture, and architecture. Historical maps give us an insight into the layout and structure of ancient Rome, helping us make sense of the city’s enormous and complex urban landscape. In this post, we’ll take a closer look at the fascinating old Roman map, dissecting its parts map of ancient rome to learn more about their significance.
The Seven Hills of Rome
Each of Rome’s seven hills played a significant role in the city’s foundation and growth. These mountains are:
- Palatine Hill: When discussing the origins of Rome, the Palatine Hill is often mentioned. It is rich in legend and history as the location of imperial palaces.
- Capitoline Hill: The Capitoline Hill served as the spiritual epicenter of ancient Rome, and it was there that the Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus was built.
- Aventine Hill: Gardens, mansions, and temples dotted the Aventine Hill, which served as a residential area for ancient Romans.
- Esquiline Hill: The Esquiline Hill was a multi-use community that was map of ancient rome home to a wide range of people, from the wealthy to the middle class to a sizable immigrant population.
- Caelian Hill: The Caelian Hill was a popular place for the wealthy and influential of Rome to call home due to its abundance of lavish mansions.
- Quirinal Hill: Residential buildings, temples, and public baths all coexisted on the Quirinal Hill.
- Viminal Hill: The Viminal Hill was the most commercial and industrial of the seven hills, housing factories and marketplaces.
The Roman Forum
The valley between the Palatine and Capitoline Hills was home to the Roman Forum, the social, political, and religious center of ancient Rome.
The Colosseum and Amphitheatres
The Colosseum was the world’s largest amphitheater when it was constructed in ancient Rome. Public shows, including gladiator fights, were held there.
The Circus Maximus
The Circus Maximus was an important cultural landmark because of its status as an ancient Roman chariot racing stadium and entertainment facility.
The Roman Walls and Gates
The ancient Roman city’s defenses and access points relied heavily on its walls and gates. One such early defensive wall that encircled a sizable area of the city was the Servian Wall.
Conclusion
Learning more about the layout and significance of different areas of ancient Rome is made possible through an examination of maps from that time period. Understanding the dynamics and urban evolution of ancient Rome is impossible to do without first gaining an appreciation for the Seven Hills, the Roman Forum, the Colosseum, the Circus Maximus, and the city’s defensive walls. The value of this great city’s history and culture can be better map of ancient rome understood through an examination of these aspects.
Frequently Ask Questions (FAQs)
What was the Roman Forum, and why was it significant?
Between the Palatine and Capitoline Hills stood the Roman Forum, the heart of ancient Rome. Political, ecclesiastical, and social life all converged there. The Roman people congregated there to conduct business, discuss politics, and worship at the city’s many temples and public marketplaces.
What is the Colosseum, and what was its purpose?
The Colosseum, or Flavian Amphitheatre, was an enormous Roman amphitheater. The arena was largely put to use for public shows including gladiator fights, animal hunts, and simulated naval warfare. It served as a showcase for Roman technical skills and is now universally recognized as a symbol of Roman civilization and its vibrant arts and entertainment scene.
What was the Circus Maximus, and what events took place there?
The Circus Maximus was a stadium in ancient Rome where chariot races were held for amusement. It was built to accommodate a huge crowd and served as the venue for chariot races. It was also a key cultural and social center in ancient Rome because it was the site of public festivals, games, and religious rites.
Tell me about the Roman defensive walls and gates.
The Roman fortifications were vital in keeping the city safe and controlling traffic. Both the Servian Wall and the later Aurelian Walls were built to protect Rome, with the latter enclosing a larger portion of the city. The walls contained gates that regulated transportation and commerce and served as additional points of defense for the city.