If you plan to expand your business into new locations, you must look at everything that goes with it. This includes a new lease for office space, more employees, and the cost of IT infrastructure and business-grade connectivity lines.
MPLS works at a layer between traditional definitions of OSI layers 2 and 3. It is designed to provide high bandwidth and competitive IP SLAs.
Scalability
In this time of soaring enterprise demand, the most critical factor in a network is its ability to manage and course traffic. MPLS is a critical player in upgrading your organization’s versatility and productivity.
When you use an MPLS solution, it creates predetermined network paths based on the performance needs of specific data types. This enables you to prioritize specific traffic classes, such as real-time (voice, video, CRM) and best effort (Internet, email), reducing latency and improving the quality of your data.
To make this happen, routers apply a label to every packet to identify a Forwarding Equivalence Class. This eliminates the need to calculate routes at each router, which makes MPLS a faster solution than traditional routing. This is why companies increasingly choose to combine MPLS and SD-WAN in their CCIE Enterprise networks and leverage direct Internet connections to branch offices for improved connectivity and performance. This is called hybrid networking. This solution can reduce network complexity and improve QoS while ensuring employees can work remotely.
Reliability
What is MPLS? The reliability of network connectivity is vital to many enterprise applications, especially those that require latency-sensitive performance. Slow or broken connections can impact employee productivity and customer experience.
Due to automated label switching and traffic engineering features, MPLS offers higher uptime than the Internet. These features allow traffic to be steered along pre-defined paths, eliminating delays caused by routers determining the best route for each packet. MPLS offers path diversity, carrier diversity, and granular control over routing decisions and failover mechanisms.
For example, real-time applications like VOIP and video conference require high-quality bandwidth with low latency times and jitter. MPLS connections can guarantee these requirements, whereas Internet connections offer only monthly averages for latency and jitter. An MPLS connection is the choice for enterprises needing reliable, consistent connectivity. However, it requires a significant investment in the private infrastructure and can be expensive to deploy and maintain. SD-WAN provides a more flexible solution that can deliver the same or better performance at a fraction of the cost.
Flexibility
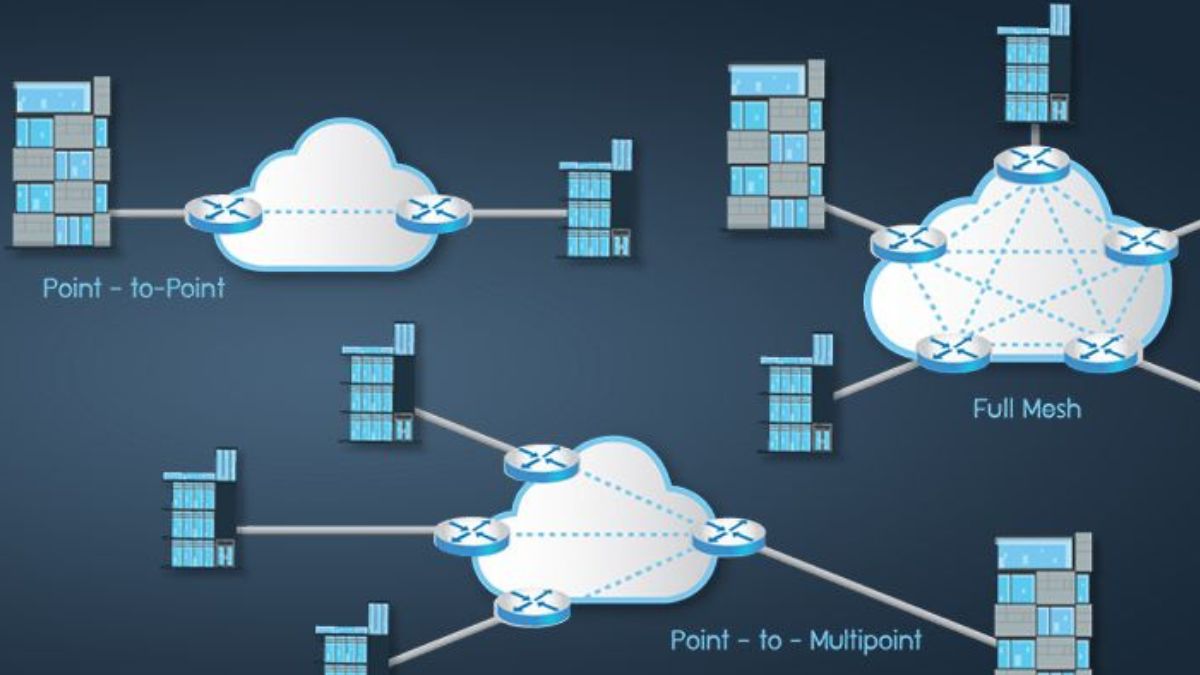
Adding a new branch office means securing a physical space, hiring additional staff, and investing in the right business-grade connectivity lines. A new site often requires connecting to the organization’s data center and applications. This typically translates to multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) or software-defined wide area networks (SD-WAN).
When network traffic is sent to the Internet, routers route it based on its destination IP address. However, this can cause a significant delay for latency-sensitive applications. MPLS provides a better solution by using labels to determine the best path for a packet. This eliminates the cumulative delays when routers recalculate routes for each packet.
As a result, MPLS delivers guaranteed delivery and real-time fast reroute protection. This is especially important for applications that require high bandwidth or a strict Service Level Agreement (SLA).
Security
MPLS is a secure network technology with a defense-in-depth strategy that protects corporate data and connections.
Instead of relying on IP routing, which operates at OSI Layer 3, MPLS allows routers to forward packets at the data link level or OSI Layer 2. As a result, routers spend less time figuring out which path to send a packet to its next destination, and as a result, the transfer process is more efficient.
In addition, MPLS can assign different classes of service to data packets, ensuring that mission-critical information gets prioritized over less critical information. This helps to ensure that your most crucial business applications get the bandwidth they need without slowing down your overall network speed. Regarding security, MPLS networks can be secured with firewalls and inline IPS systems to keep sensitive data safe.
Scalability
MPLS is a highly scalable protocol for network communications. It splits packets into small chunks to process and send them faster than previous network technologies. It also breaks down the information in each packet so routers can search their routing tables for a particular destination only partially.
This allows the routers to direct data by the label instead, reducing processing resources and speeding up transmission time. As each router passes the packet, it uses the information in its label to determine where to go next — a process called forwarding equivalence. When the packet reaches its final destination, the label is removed, and the packet is sent as standard IP data.
As an enterprise grows, it may require more networking infrastructure to meet its connectivity and performance needs. However, introducing more site locations can quickly add to an expensive investment. That is where alternative technologies like SD-WAN come in. They can help organizations augment their MPLS with affordable internet connections at their branch offices, optimizing bandwidth and security based on application and network performance requirements.