Multifocal pneumonia is a condition that can send chills down your spine, especially in the midst of the global COVID-19 pandemic. With respiratory illnesses at the forefront of our minds, understanding this particular form of pneumonia becomes even more crucial. But fear not! In this blog post, we’ll unravel the mysteries surrounding multifocal pneumonia, exploring its symptoms, causes, and treatment options. So buckle up and get ready for an insightful journey into the world of multifocal pneumonia!
What is Multifocal Pneumonia?
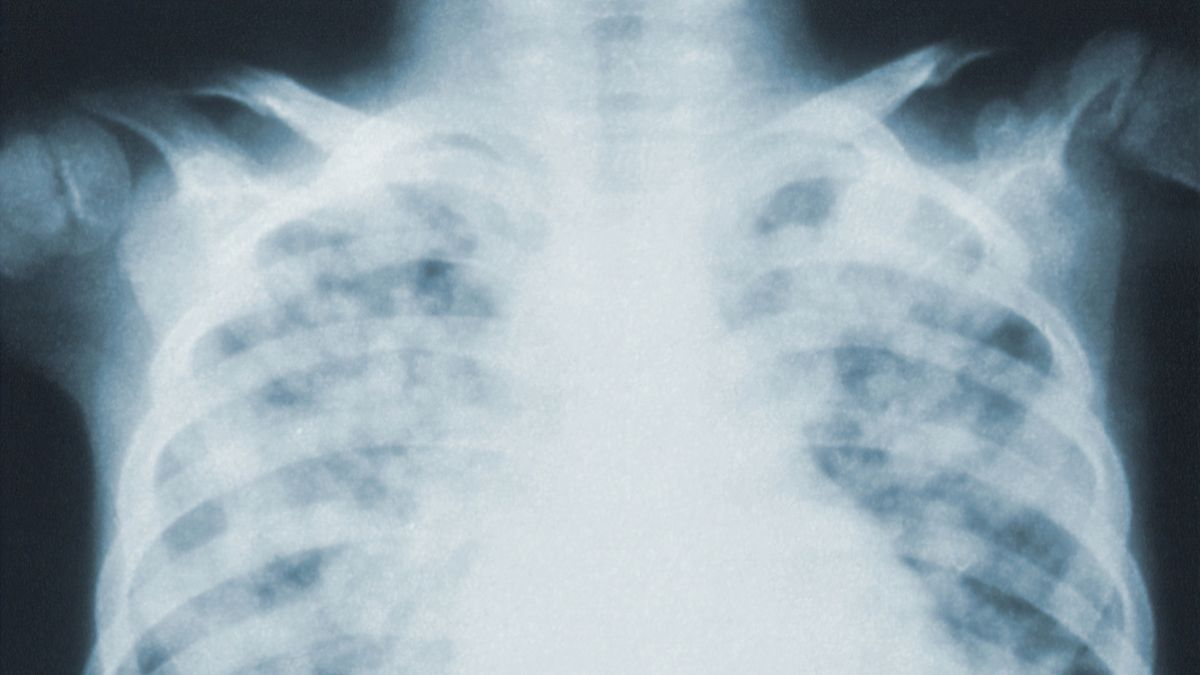
Multifocal pneumonia is a type of lung infection that affects multiple areas or lobes of the lungs simultaneously. Unlike typical pneumonia, which usually only affects one lobe, multifocal pneumonia can cause inflammation and infection in several areas of the lungs at once.
This condition can be caused by various factors such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, or a combination of these microorganisms. It often occurs in individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions that make them more susceptible to respiratory infections.
Symptoms of multifocal pneumonia may include fever, coughing (with or without phlegm), shortness of breath, chest pain when breathing or coughing, fatigue, and weakness. These symptoms can range from mild to severe depending on the extent and severity of the infection.
Diagnosing multifocal pneumonia typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, imaging tests such as X-rays or CT scans, and laboratory analysis of sputum samples to identify the causative agent.
Treatment options for multifocal pneumonia will depend on the underlying cause and severity. Antibiotics are commonly prescribed for bacterial infections while antiviral medications may be used against viral pathogens. Supportive care measures such as rest, hydration,
and over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage symptoms and promote recovery.
It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent respiratory symptoms or suspect you may have multifocal pneumonia. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial in preventing complications and promoting faster recovery.
Definition of Multifocal Pneumonia
Multifocal pneumonia is a medical condition that affects the lungs and causes inflammation in multiple areas, known as foci. These foci are scattered throughout both lungs, making it different from typical pneumonia where the infection is confined to one specific area. This type of pneumonia can be challenging to diagnose and treat due to its widespread nature.
In multifocal pneumonia, the infection can affect various parts of the respiratory system simultaneously. The inflammation spreads rapidly, leading to symptoms such as coughing, difficulty breathing, chest pain, and fever. It can also result in complications if left untreated.
This condition often occurs in individuals with weakened immune systems or underlying health conditions. Risk factors include advanced age, chronic lung diseases like COPD or asthma, HIV/AIDS, cancer treatments like chemotherapy or radiation therapy, organ transplants requiring immunosuppressive medications.
Various microorganisms can cause multifocal pneumonia including bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus; fungi like Candida species; viruses such as influenza virus and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). In recent times amidst the global COVID-19 pandemic, there have been reported cases of daptomycin-induced eosinophilic pneumonia causing multifocal involvement of the lungs.
Diagnosing multifocal pneumonia involves a combination of physical examination findings along with imaging tests such as chest X-rays or CT scans. Sputum cultures may be done to identify the causative organism.
Treatment options for multifocal pneumonia typically involve antibiotics for bacterial infections while antiviral medications are used for viral causes. Supportive care measures including rest and staying hydrated help alleviate symptoms and boost recovery.
It’s crucial to seek medical attention if you experience persistent respiratory symptoms or suspect you may have multifocal pneumonia. Early diagnosis and treatment play a vital role in managing this condition effectively and reducing complications associated with it.
Explanation of Multifocal Pneumonia Amidst the Global COVID-19 Pandemic: A Case of Daptomycin-Induced Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Amidst the global COVID-19 pandemic, it is crucial to understand the different types of pneumonia that can affect individuals. One such type is multifocal pneumonia, which can present unique challenges in diagnosis and treatment. In a recent case study, researchers discovered an interesting connection between daptomycin, a commonly used antibiotic, and the development of eosinophilic pneumonia.
Eosinophilic pneumonia occurs when there is an excessive buildup of white blood cells called eosinophils in the lung tissue. This condition can be triggered by various factors including medications like daptomycin. The study highlighted a specific case where a patient developed multifocal pneumonia after receiving treatment with daptomycin for another infection.
The link between multifocal pneumonia and daptomycin-induced eosinophilic pneumonia sheds light on the complexity of diagnosing and treating this condition amidst the ongoing COVID-19 crisis. With healthcare resources stretched thin due to the pandemic, it becomes even more critical for medical professionals to consider all possible causes when dealing with cases of multifocal pneumonia.
As we navigate through these challenging times, it is important for both healthcare providers and patients to be aware of this potential complication associated with certain medications. By staying informed and vigilant, we can ensure timely diagnosis and appropriate management of multifocal pneumonia cases related to drug reactions like daptomycin-induced eosinophilic pneumonia.
Causes of Multifocal Pneumonia
Multifocal pneumonia can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from underlying health conditions to exposure to certain microorganisms. Understanding the potential causes is crucial in preventing and treating this condition effectively.
One of the key risk factors associated with multifocal pneumonia is a weakened immune system. Individuals with conditions such as HIV/AIDS, cancer, or those who have undergone organ transplantation are more susceptible to developing pneumonia in multiple areas of their lungs.
In addition to compromised immunity, various bacteria, fungi, and viruses can also lead to multifocal pneumonia. Common culprits include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, Legionella pneumophila, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). These pathogens can enter the lungs through inhalation or spread from another part of the body.
Furthermore, environmental factors such as pollution or occupational exposures may contribute to the development of multifocal pneumonia. Inhalation of harmful substances like chemicals or dust particles can irritate the airways and potentially trigger an inflammatory response that leads to infection.
It’s important to note that amidst the global COVID-19 pandemic, there have been cases where medications like daptomycin have been linked to inducing eosinophilic pneumonia in some individuals. This serves as a reminder that drug-induced reactions can also be a cause for multifocal pneumonia.
By understanding these potential causes and risk factors associated with multifocal pneumonia, healthcare professionals can better diagnose and treat patients while implementing preventive measures for those at higher risk. Early identification and appropriate management play vital roles in minimizing complications and promoting recovery.
Risk Factors Associated with Multifocal Pneumonia
Multifocal pneumonia is a serious respiratory condition that can affect individuals of all ages. While anyone can develop multifocal’pneumonia, certain factors may increase the risk of experiencing this condition.
Age plays a significant role in the development of multifocal pneumonia. Older adults, particularly those over the age of 65, are more susceptible to infections due to a weakened immune system. Their bodies may have difficulty fighting off bacteria or viruses that cause pneumonia.
Underlying health conditions can also contribute to an increased risk of developing multifocal’pneumonia. Individuals with chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, or asthma have compromised immune systems and are more vulnerable to respiratory infections.
Lifestyle choices such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can weaken the immune system and make individuals more prone to developing multifocal pneumonia.
Certain environmental factors can also increase the risk of acquiring multifocal’pneumonia. Exposure to pollutants or chemicals in the workplace or living environment can irritate and damage lung tissues, making it easier for pathogens to invade and cause infection.
It is important for individuals who fall into these high-risk categories to take precautions by practicing good hygiene habits like regular handwashing and getting vaccinated against common respiratory illnesses like influenza and pneumococcal disease. Additionally, seeking prompt medical attention at any sign of symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment.
Bacteria, Fungi, and Viruses that can Cause Multifocal Pneumonia
Multifocal pneumonia can be caused by a variety of infectious agents, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. These microorganisms invade the lungs and lead to inflammation and infection in multiple areas or lobes of the lungs.
Bacterial infections are one of the common culprits behind multifocal pneumonia. Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Staphylococcus aureus, and Klebsiella pneumoniae are some examples of bacteria that can cause this condition. These bacteria are usually spread through respiratory droplets or direct contact with contaminated surfaces.
Fungal infections can also contribute to multifocal pneumonia. Candida species, Aspergillus species, and Pneumocystis jirovecii are among the fungi known to cause lung infections. Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those living with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy treatment for cancer, are particularly susceptible to fungal-related multifocal pneumonia.
Viruses play a significant role in causing respiratory infections, including multifocal pneumonia. Influenza viruses (such as H1N1), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), adenovirus, and coronavirus (including SARS-CoV-2) have all been associated with cases of multifocal pneumonia. Viral respiratory infections often spread through coughing or sneezing.
It’s important to note that these microorganisms can infect individuals of any age group but may pose higher risks for older adults or people with underlying health conditions. Understanding the diverse range of infectious agents that can cause multifocal pneumonia is crucial for prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment interventions.
Symptoms of Multifocal Pneumonia
Multifocal pneumonia can present with a range of symptoms, which can vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the infection. It is important to be aware of these symptoms in order to seek timely medical attention.
One common symptom is a persistent cough that may produce phlegm or mucus. This cough can be accompanied by chest pain or discomfort, making it difficult to breathe deeply. Some individuals may also experience shortness of breath or wheezing, especially during physical activity.
In addition to respiratory symptoms, multifocal pneumonia can also manifest as fever and chills. The body’s natural response to infection often includes an increase in body temperature, leading to fever. Chills may accompany the fever as well.
Other possible symptoms include fatigue, muscle aches, and headache. These general malaise symptoms are non-specific but can be indicative of an underlying infection such as multifocal pneumonia.
It is important not to ignore these symptoms if they persist or worsen over time. Seeking medical attention promptly will help ensure appropriate diagnosis and treatment for multifocal pneumonia.
Diagnosis of Multifocal Pneumonia
Detecting multifocal’pneumonia can be a complex task for healthcare professionals. The symptoms may overlap with other respiratory conditions, making it challenging to pinpoint the exact cause. However, several diagnostic tests and techniques can help in accurately diagnosing this condition.
The doctor will conduct a thorough physical examination and review your medical history. They will listen to your lungs using a stethoscope to check for abnormal sounds such as crackles or wheezes that indicate lung inflammation. Additionally, they may inquire about any recent illnesses or exposure to potential pathogens.
To confirm the diagnosis, chest imaging is crucial. A chest X-ray or computerized tomography (CT) scan can provide detailed images of the lungs and reveal any abnormalities such as consolidation or infiltrates characteristic of multifocal’pneumonia.
In some cases, laboratory tests are necessary to identify the specific causative organism responsible for the infection. These may include blood tests, sputum culture analysis, or even bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid analysis.
Early and accurate diagnosis of multifocal’pneumonia is vital to ensure prompt initiation of appropriate treatment. If you experience persistent coughing, shortness of breath, fever, or other respiratory symptoms that worsen over time – don’t hesitate to seek medical attention! Your healthcare provider will guide you through the necessary diagnostic steps needed for an accurate diagnosis and effective management plan.
Treatment Options for Multifocal Pneumonia
When it comes to treating multifocal’pneumonia, a comprehensive approach is necessary to effectively address this condition. The treatment options for multifocal pneumonia may vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the infection.
The primary goal of treatment is to eliminate the infection and prevent complications. In most cases, antibiotics are prescribed to combat bacterial infections that can lead to multifocal’pneumonia. It is crucial to ensure that the chosen antibiotic is effective against the specific bacteria causing the infection.
In addition to antibiotics, antifungal medications may be used if fungi are identified as the causative agents. Antiviral drugs might also be employed in cases where viruses contribute to multifocal’pneumonia.
Supportive care plays an essential role in managing symptoms and aiding recovery. This includes ensuring adequate rest, maintaining hydration through intravenous fluids or oral rehydration solutions, and providing oxygen therapy when needed.
In severe cases of multifocal’pneumonia, hospitalization may be required for closer monitoring and intensive treatment measures such as mechanical ventilation or oxygenation support.
Remember, early detection and prompt intervention are key factors in successfully treating multifocal’pneumonia. If you experience any symptoms associated with this condition or have concerns about your respiratory health, it is vital to seek medical attention promptly for appropriate diagnosis and tailored treatment options.
Complications of Multifocal Pneumonia
Multifocal pneumonia, like any other respiratory infection, can lead to various complications if left untreated or not managed effectively. These complications can range from mild to severe and may require additional medical interventions.
One common complication of multifocal pneumonia is the development of pleural effusion. This occurs when fluid accumulates in the space between the lung and chest wall, causing discomfort and difficulty breathing. If left untreated, pleural effusion can progress to more serious conditions such as empyema, a collection of pus in the pleural cavity.
Another potential complication is respiratory failure. Severe cases of multifocal pneumonia can lead to significant inflammation and damage to lung tissue, impairing its ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide efficiently. This may result in low blood oxygen levels and necessitate supplementary oxygen or even mechanical ventilation support.
In some instances, multifocal pneumonia can give rise to sepsis—a potentially life-threatening condition where an infection spreads throughout the body via the bloodstream. Sepsis requires immediate medical attention due to its association with organ dysfunction and increased mortality rates.
Recurrent episodes of multifocal’pneumonia can weaken the immune system over time, making individuals more susceptible to future infections. This highlights the importance of prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment measures in order to minimize these long-term consequences.
It is crucial for individuals diagnosed with multifocal’pneumonia or those at risk for developing this condition (such as older adults or those with weakened immune systems) seek early medical intervention to prevent complications from arising or worsening further.
Conclusion
Multifocal’pneumonia is a serious condition that can have various causes and present with a range of symptoms. It is important to understand the risk factors associated with multifocal’pneumonia, including underlying health conditions and exposure to certain bacteria, fungi, or viruses.
Early diagnosis is crucial in managing this condition effectively. Healthcare professionals employ various diagnostic techniques such as imaging tests and laboratory analysis to confirm the presence of multifocal’pneumonia.
Treatment options for multifocal’pneumonia typically involve antibiotic or antifungal medications targeting the specific causative agent. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required for closer monitoring and more aggressive treatment approaches.
It is essential to follow prescribed treatment regimens diligently and complete the full course of medication to ensure effective eradication of infection. Additionally, taking steps to prevent respiratory infections through good hygiene practices can help reduce the risk of developing multifocal’pneumonia.
Although complications may arise from multifocal’pneumonia, timely medical intervention along with proper care and management significantly improves outcomes. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are recommended for those at higher risk or who have previously experienced episodes of multidrug-resistant pathogens causing recurrent multifocal’pneumonia.
By staying informed about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis methods, treatment options, and potential complications associated with multifocal’pneumonia, individuals can take proactive measures towards better lung health. Understanding this condition empowers us all to prioritize our well-being while promoting awareness within our communities.
ALSO READ: Is Sinus Infection Contagious? Exploring the Transmission and Spread of Sinusitis