To treat fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity, doctors may use a surgery called paracentesis. Abdominal tapping is a treatment that serves both diagnostic and therapeutic objectives. In this post, we’ll go through the technique, its applications, and the dangers that may be involved.
Understanding Paracentesis
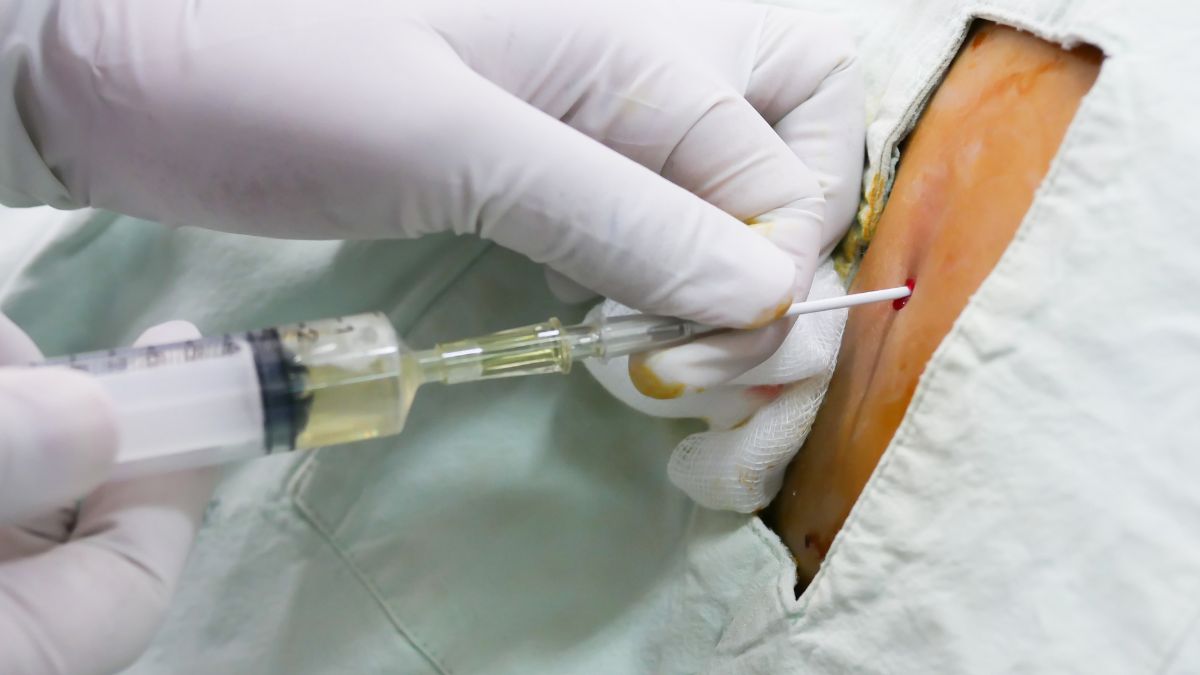
Paracentesis is an outpatient or inpatient technique that requires minor incisions. The patient will be asked to lie on their back while an antiseptic solution is used to clean the area around their navel. The site where the needle or catheter will be put will be numbed with a local anesthetic before the procedure begins. The next step is to insert the needle or catheter through the lower abdominal wall and into the abdominal cavity. The needle or catheter is inserted, and the fluid is emptied into a sterile container.
Uses of Paracentesis
Paracentesis has dual therapeutic and diagnostic applications. The following are examples of typical applications of paracentesis:
- Diagnostic purposes: The procedure of paracentesis can be used to determine the source of abdominal fluid accumulation. The diagnosis of cancer, cirrhosis of the liver, and other diseases may benefit from this.
- Therapeutic purposes: The accumulation of fluid in the abdomen can cause discomfort, but paracentesis can help. Ascites is a common complication of liver illness, and this can be useful in treating the problem.
- Monitoring: Paracentesis can be done to check up on the development of diseases including cancer and liver disease.
Risks of Paracentesis
Paracentesis, like any other medical operation, is not without its hazards. Paracentesis carries with it a number of possible dangers, including:
- Infection: The insertion site of a needle or catheter is vulnerable to infection.
- Bleeding: When a needle or catheter is placed into the body, bleeding might occur.
- Organ damage: Incorrect insertion of the needle or catheter might cause serious injury to the organ.
- Low blood pressure: Some individuals may experience a life-threatening decline in blood pressure during paracentesis.
- Fluid and electrolyte imbalances: Fluid and electrolyte imbalances, which paracentesis is known to create, can be life-threatening for some patients.
Additional Information on Paracentesis
Preparation for Paracentesis
Your healthcare practitioner will offer you detailed advice on how to get ready for paracentesis. Examples of such things could be:
- Preparing for the procedure by fasting for a specified amount of time.
- Not taking blood-thinning drugs like aspirin, which can increase the risk of bleeding.
- Sharing all relevant medical history and allergy information with your doctor.
- You should make plans to have someone take you home following the surgery because you may be too weak to drive.
During the Procedure
You will lie on your back while your doctor uses an ultrasound or other imaging technique to find the fluid-filled area in your abdomen. An antibiotic will be used to disinfect the region before a local anesthetic is injected to numb the skin and any underlying tissues.
After making an incision in your skin, a small needle or catheter will be inserted into the cavity. Draining the fluid into a clean container allows for more thorough examination.
The process takes around 30 seconds to an hour, depending on how many mistakes you make.
After the Procedure
There could be some post-operative pain or tenderness at the site of implantation. Your doctor may advise you to take pain relievers available without a prescription.
- Infection symptoms including redness, swelling, or discharge from the insertion site may raise concern. If you have a high temperature, chills, or any other concerning symptoms, you should make an appointment with your doctor right once.
- You may feel some pain or tenderness at the insertion site once the surgery has been completed. Your doctor may advise you to try over-the-counter pain relievers to see if they help.
- Symptoms of infection at the insertion site include redness, edema, and discharge. If you have a high temperature, chills, or any other concerning symptoms, you should consult your doctor immediately.
Final Thoughts
The medical process known as paracentesis has dual goals in the medical world: diagnosis and treatment. It’s a little operation, so the dangers are low, but they’re still there. The risks and benefits of paracentesis should be discussed in detail with your doctor before the surgery is performed.
In a wide range of medical settings, paracentesis has shown to be an invaluable diagnostic and therapeutic technique. If conducted by a trained medical professional, it is a risk-free and very efficient treatment option. Knowing the benefits and hazards of paracentesis will help you decide if it’s the correct choice for you.