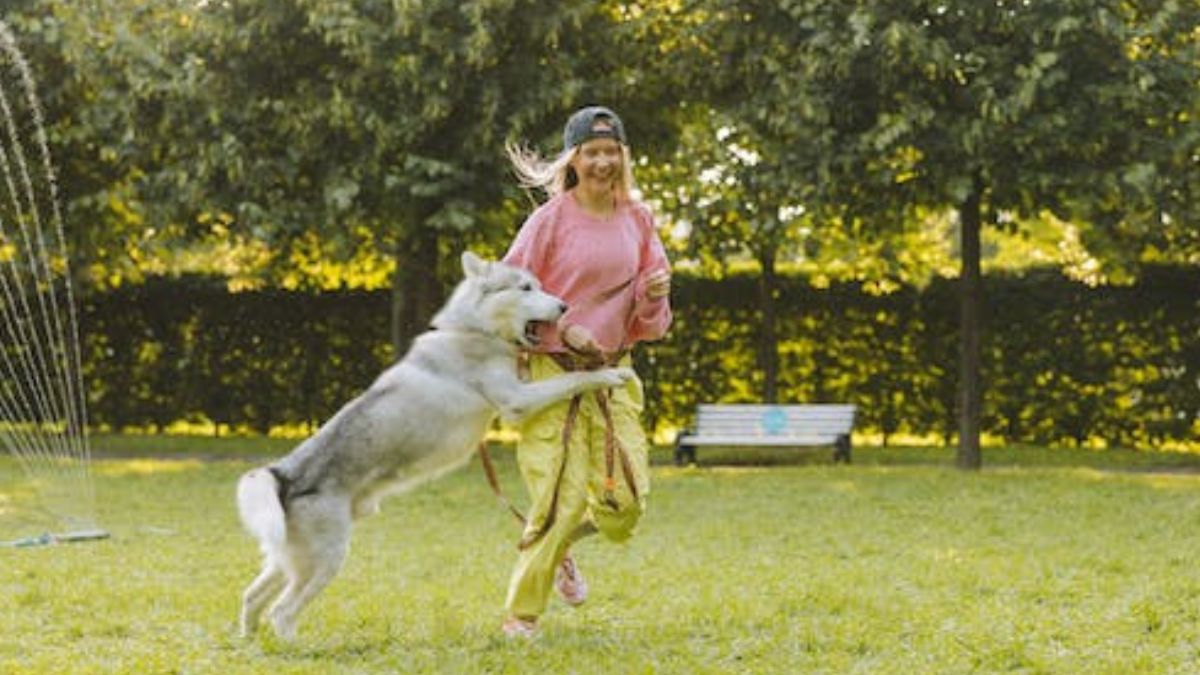
Safety and security have risen to the top of the list of concerns for individuals and families in today’s unpredictable environment. The training and ownership of a personal protection dog is one proactive and efficient method of self-defense. These dogs are so well trained that they not only make people feel safer, but also serve as a deterrent to would-be attackers. In this post, we’ll take a look at the fundamentals of training a dog for personal protection and the advantages that can bring to people who want to feel safer in their own skin.
What is Personal Protection Dog Training?
The purpose of personal protection dog training is to teach dogs to defend their human family and the things they hold dear. Personal protection dog training teaches canines advanced ways to recognize and respond to potential dangers, as opposed to the more fundamental instructions and behavior emphasized in standard obedience training.
The Training Process
- Selecting the Right Breed: Unfortunately, not all canine species are cut out for the role of bodyguard. Dogs of the German Shepherd, Belgian Malinois, Rottweiler, and Doberman Pinscher breeds are frequently used in this capacity. These breeds were selected for their innate qualities of brains, loyalty, brawn, and quickness to pick up new skills.
- Professional Trainer: It is essential to hire a dog trainer with extensive experience in teaching guard dogs how to protect their owners. In order to determine whether or not a dog is suitable for personal protection employment, these trainers must first evaluate its disposition.
- Basic Obedience: The dog should be able to sit, stay, come, heel, and down before beginning personal protection training. These instructions establish the trainer’s authority and control over the dog and form the basis for further training.
- Socialization: Incorporating socialization into the training of a personal security dog is essential. For a dog to get the self-assurance, flexibility, and command it needs, it must be exposed to a wide range of experiences and people. The ability to distinguish between friends and foes depends on a dog’s level of socialization, which is why it’s so important.
- Bite Work and Defensive Techniques: Teaching the dog the appropriate reactions to potential dangers is a crucial part of personal protection training. Dogs can be trained to successfully apprehend an attacker through controlled bite work. The training focuses on controlled aggression and biting inhibition to keep the dog and the person safe.
Benefits of Personal Protection Dog Training
- Enhanced Personal Safety: Having a dog with you can help deter any unwanted attention. Simply having them around can deter would-be thieves, intruders, and assailants. A personal protection dog is a canine specifically trained to guard its owner from harm and to alert others to the existence of danger.
- Peace of Mind: For those who live alone, travel frequently, or work in dangerous locations, having a personal protection dog can provide a welcome sense of safety and peace of mind. Anxiety and panic can be greatly diminished when one realizes they have a trustworthy friend by their side.
- Companionship and Bonding: Training a dog to be a personal security animal strengthens the attachment between the two of you. Relationships built on mutual respect and understanding are strengthened via the shared training experiences and regular interaction.
- Family Protection: Family members are also protected by personal protection dogs. They are a priceless asset to home security because they may be taught to identify and respond to threats against family members.
However, keep in mind that owning a personal protection dog is a huge commitment, and both the dog’s and owner’s safety depend on them receiving regular training and care.
Ongoing Maintenance and Care
To keep a dog in top form as a personal security animal, it must get regular training, socializing, and upkeep. Here are a few things to keep in mind when caring for a personal protection dog:
- Continued Training: Training a dog for personal defense is an ongoing process. Maintaining the dog’s skills and keeping it attentive to commands calls for consistent reinforcement and practice. Professional training sessions should be scheduled on a regular basis to help them develop their skills and overcome any behavioral challenges.
- Physical Exercise: Keeping a personal protection dog healthy and mentally occupied calls for regular exercise, as these dogs tend to be high-energy and energetic breeds. To maintain peak physical condition and forestall boredom-related behavioral issues, regular walks, runs, and play sessions are required.
- Mental Stimulation: Protection dogs need cerebral stimulation in addition to physical activity to prevent boredom and retain focus. Keeping them occupied with games that require them to use their brain, such as puzzle toys, scent work, or obedience training, keeps them alert and focused.
- Proper Socialization: Maintaining a dog’s confidence and good behavior in new situations and around new people and other animals requires consistent socialization throughout the animal’s life. When people are regularly exposed to different environments, activities, and people, they are less likely to acquire anxiety or aggressive tendencies.
- Veterinary Care: The health and well-being of a dog used for personal protection depends on it receiving routine veterinarian care, including checkups, vaccines, and preventative treatments. Proper dog care includes keeping up with vaccines, treating for parasites, and feeding a balanced diet.
Legal Considerations
Understanding the legal implications of having a personal protection dog is essential. Personal protection dog ownership, training, and use laws and restrictions might differ by region. Before beginning training for a personal protection dog, it is wise to familiarize oneself with the relevant local rules and regulations.
Despite the fact that they have been trained to effectively respond to danger, personal protection dogs should never be employed in a violent or offensive manner. Training and ownership based on responsibility stress self-control and the ability to distinguish between real and perceived dangers.
Conclusion
Training a dog specifically for personal protection is a niche field that can give people and their families peace of mind. Personal protection dogs can be wonderful friends and deterrents against would-be aggressors if their training is properly initiated, supervised, and maintained. However, training a dog for personal protection must be approached with seriousness, accountability, and concern for the dog’s well-being and safety. This strengthens the link between the owner and their well trained dog, and it also makes the owner safer.