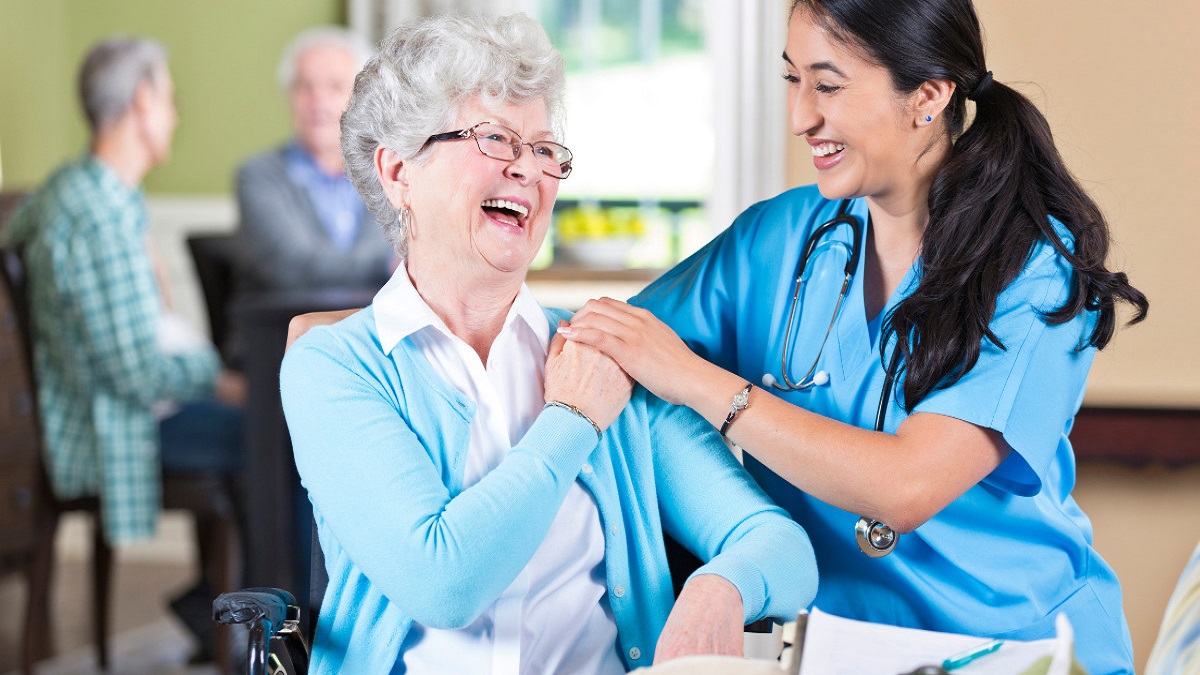
Introduction
Our bodies and minds require more care and attention as we age. But aging doesn’t have to be a journey of decline; instead, it provides opportunities for meaningful, active, and fulfilling lives despite declining capacities. One keystone that helps make this possible is occupational therapy. By viewing it through the lens of ability rather than disability, it provides opportunities for an enhanced quality of life in later years.
What is Occupational Therapy?
Occupational therapy (OT) is a holistic form of healthcare designed to enable individuals of all ages to live their best lives by helping them overcome physical, mental, or cognitive barriers that limit daily activities or “occupations,” such as dressing, eating and bathing, work activities or hobbies or social gatherings.
Head over to Oxa Care to find out more about aged care services.
The Role of Occupational Therapists
Occupational therapists play an invaluable role in this process. By assessing an individual’s physical, mental, and social needs and creating a personalised therapeutic plan tailored specifically for them to increase independence in performing essential daily tasks – they offer customised solutions centred on each person’s wants, needs, and goals – rather than providing generic solutions tailored towards universality.
Occupational Therapy in Aged Care
As people age, they face various challenges that impede their ability to engage in everyday tasks. These could range from chronic health conditions or cognitive changes, reduced mobility issues or environmental obstacles; occupational therapy aged care provides tailored strategies that empower seniors to live fuller, independent lives.
Enhancing Daily Living Skills
Aged care occupational therapy primarily focuses on increasing an individual’s capacity for activities of daily living (ADLs), such as bathing, dressing, eating and mobility. An occupational therapist will evaluate an elderly resident’s functional abilities before developing strategies to increase these capabilities.
For instance, if an older individual with arthritis struggles to dress efficiently and pain-free, an occupational therapist might demonstrate techniques and suggest assistive devices like long-handled shoe horns or button hooks to promote independence and encourage independence.
Promoting Social Engagement and Mental Health
Aging can often result in feelings of isolation or mental health conditions like depression. Occupational therapy recognises the significance of social engagement and mental well-being for seniors. They work to develop strategies that enable older individuals to participate in leisure activities or social interactions they find meaningful – improving their quality of life and mental well-being significantly.
Home and Environmental Modifications
One of the hallmarks of occupational therapy in aged care is its focus on an individual’s environment. Occupational therapists will typically assess living spaces to ensure they are safe, accessible, and supportive of an individual’s needs – this may involve installing grab bars in bathrooms or rearranging furniture to improve mobility and suggesting adaptive equipment that makes tasks more accessible and safer.
Advancing Quality of Life through Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy offers an innovative solution for aged care, encouraging independence, self-esteem, and overall quality of life. The benefits extend beyond physical health alone to cover mental, emotional and social well-being.
Physical Health and Mobility
Occupational therapy can significantly benefit older adults by helping them better manage daily activities and decrease the risk of falls, one of the primary sources of injury among seniors. Furthermore, occupational therapy teaches older people how to manage chronic conditions more effectively, leading to a healthier life overall.
Mental and Emotional Well-being
Occupational therapy goes beyond physical health and considers an individual’s mental and emotional well-being. By engaging seniors in meaningful activities, occupational therapy can improve mood, alleviate feelings of isolation and enhance overall life satisfaction.
Independence and Autonomy
At its core, occupational therapy is a holistic and client-centric approach designed to foster independence and boost well-being among different age groups. Seniors can significantly benefit from occupational therapy in providing autonomy and self-sufficiency in daily life with professional guidance from occupational therapists who offer specialist support services; with such advice, they can overcome physical, cognitive and emotional obstacles more quickly in engaging in meaningful activities and reaching personal goals faster.
Conclusion
Occupational therapy is more than a healthcare service; it’s an approach to life that views aging as an opportunity to keep learning and growing. When caring for seniors in their golden years, occupational therapy provides a compassionate yet holistic approach that recognises and addresses unique challenges they may encounter. Through occupational treatment, we can pave the way to happier, healthier, more independent later years by strengthening everyday living skills, increasing social engagement opportunities, and adapting environments accordingly.