In today’s high-tech electrical systems, transformers are needed for voltage transformer safety, regulation and reliable power delivery. However, if proper safety measures are not taken, working with transformers can be extremely dangerous. The hazards of dealing with transformers, how to prevent injury when handling them, and the best methods for doing so are all topics we’ll cover in this article.
Understanding Transformers
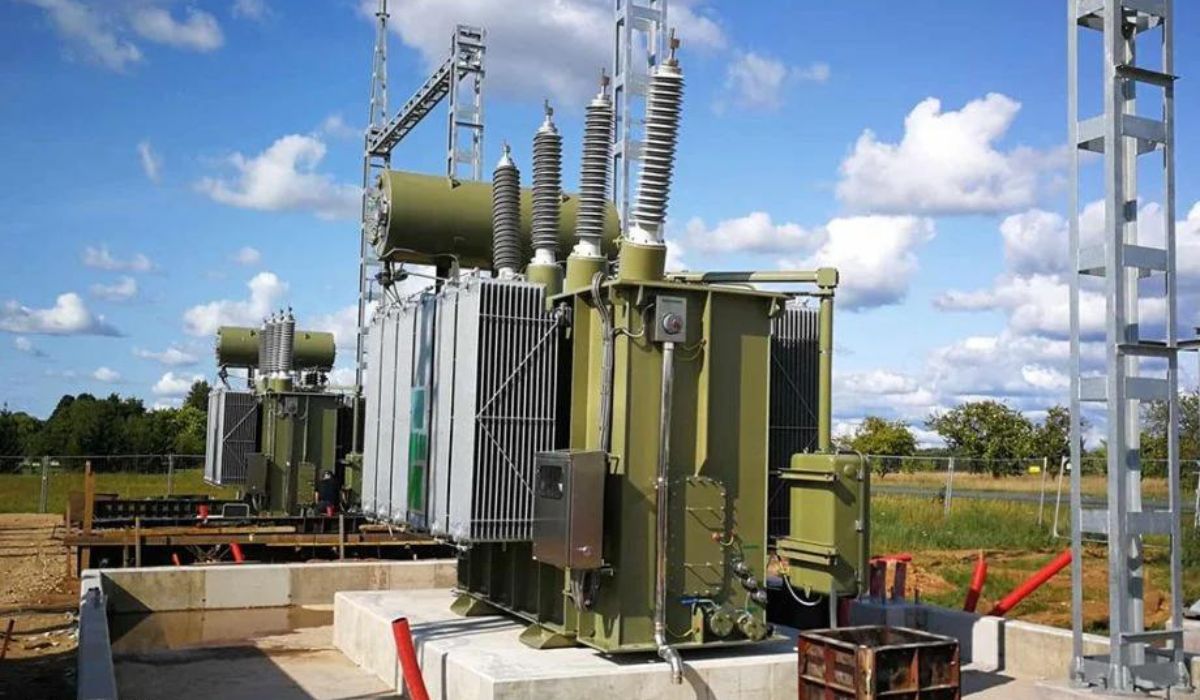
Knowing what a transformer is and how it operates is a prerequisite to learning about transformer safety. In order to move electricity from one circuit to another, transformers use electromagnetic induction. The windings, both primary and secondary, are typically twisted around a magnetic core. Depending on the need, transformers can either increase or decrease voltage levels.
Importance of Transformer Safety
The safety of transformers is crucial for preventing injuries and property loss. Electrical shock, fires, and pollution can all come from ignoring safety precautions. Accidents, downtime, and the proper operation of electrical systems can all be avoided with a focus on transformer safety.
Potential Hazards of Transformers
There are a number of risks associated with transformers that must be mitigated. In order to take adequate precautions, it is essential to be aware of these risks.
Electrical Hazards
One of the main dangers of using a transformer is the potential of electrical shock. Arc flashes, electrocution, and electric shock are all potential outcomes. If safety measures are not implemented, exposure to the high voltages and currents running through transformers can be fatal.
Fire Hazards
Due to electrical problems, overheating, or insulation failures, transformers can also provide a fire threat. The potential for fire is heightened by the presence of combustible materials, insufficient cooling systems, and lax maintenance procedures.
Environmental Hazards
Some of the materials used in transformers are toxic if released into the wild. Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are toxic to humans and the environment, and they may be present in older transformers. Transformers can pollute the environment if they are not handled, maintained, or disposed of properly.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection
In order to catch problems early and avoid mishaps, transformers require routine inspection and maintenance. This involves assessing protection devices, verifying temperatures and oil levels, and ensuring that all connections are tight.
Proper Installation and Grounding
For safe operation, transformers require proper installation and grounding. Electrical problems can be reduced by installing transformers in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, which call for certain clearances, ventilation, and grounding to be in place.
Protection Systems
Transformers can benefit from an additional layer of safety provided by the installation of appropriate protective systems including overcurrent protection, short-circuit protection, and ground fault protection. In this way, problems can be identified and corrected before they become catastrophic.
Training and Education
Accidents involving transformers can be avoided with proper training and education of workers. Workers can safely handle transformers if they have a firm grasp on electrical risks, safe work standards, and emergency protocols.
Safety Equipment
When dealing with transformers, it is imperative to use the proper safety gear. Electrical and fire threats necessitate the use of personal protection equipment (PPE), such as insulating gloves, safety glasses, and flame-resistant clothes.
Transformer Safety Practices
Transformer safety procedures must be strictly followed to ensure a risk-free workplace. The following are recommended procedures:
Risk Assessment
Before working on transformers, it is important to do a complete risk assessment in order to identify potential dangers and implement adequate safety measures. This entails checking for things like high voltage, difficulty of access, and the existence of combustible or poisonous materials.
Lockout/Tagout Procedures
Lockout/tagout procedures must be followed whenever the transformer must be de-energized for any reason, including maintenance and repairs. By following these steps, you may be confident that no one will get shocked by unintentionally turning on a power switch.
Personal Protective Equipment
It’s crucial that employees safeguard themselves by always donning the necessary PPE. When working with transformers, it is important to wear protective equipment including insulating gloves, safety goggles, hard hats, and flame-resistant clothes.
Safe Work Practices
Preventing workplace accidents requires employing safe work practices such keeping the workplace neat and tidy, using the correct processes, and not cutting corners. A secure workplace benefits from open lines of communication, cooperative efforts, and strict respect to safety regulations.
Conclusion
Protecting workers, avoiding accidents, and ensuring the stable operation of electrical networks all depend on the safe use of transformers. We can build a safe working environment that reduces risks and maximizes productivity by learning about the possible dangers posed by transformers, putting those precautions into practice, and adhering to best practices.