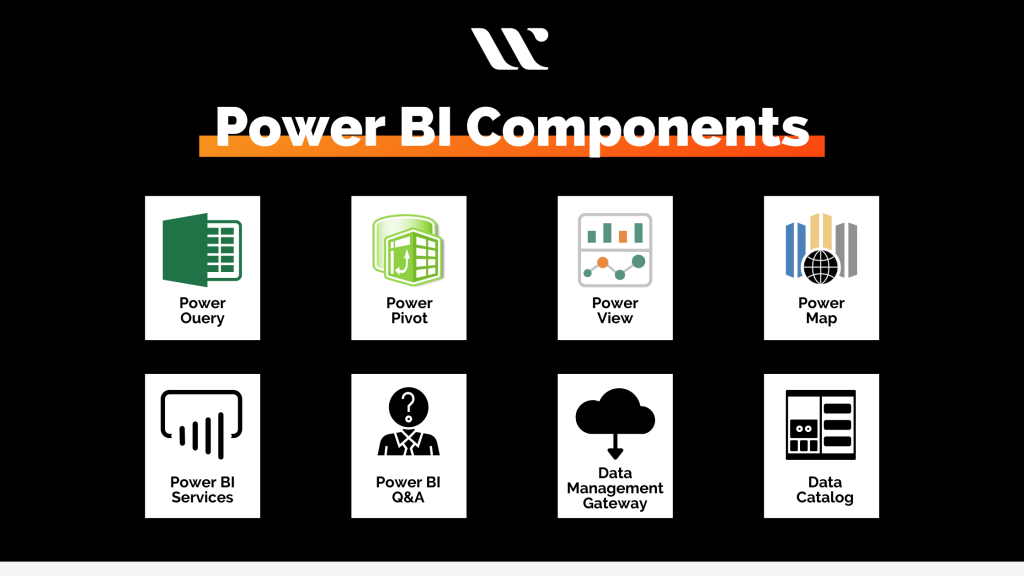
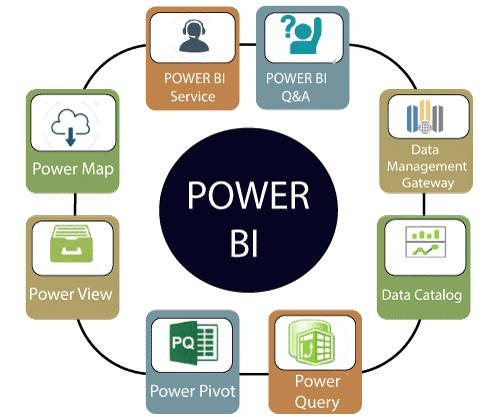
Data analysts utilize Microsoft Power BI, one of the best business intelligence tools available. Additionally, the majority of businesses used this top BI solution to manage their data efficiently at a reasonable cost and to make wise judgements when needed. There are 13 primary components in Power BI, each of which may be utilized separately to further transform and simplify the data. Now let’s explore the most often used Power BI components.
Enumeration of Microsoft Power BI Elements
Power BI comes with its own building elements for business customers, which are called Power BI content. These are as follows:
What Constitutes Power BI’s Building Blocks?
The foundation of Power BI’s operation are its five primary tools, which are as follows:
1. DataSets
Datasets are collections of imported data or the source data used in Dataflow. To save all of these datasets in one location, they are linked to Power BI.
2. Illustration
Visualization is the process of representing data using charts, graphs, diagrams, or other visual aids. These aid in reorganizing the facts to improve comprehension.
3. Reports
Reports are the graphical depictions of any gathered data, and they can include treemaps, graphs, charts, and maps. These reports may be made in Power BI and sent to friends via dashboards. When a user connects to different datasets from their Excel workbooks or SaaS services, this is an additional method of generating reports. There are two options for creating reports: Reading View and Editing View.
4. Dashboards
Dashboards are single sheets with several widgets and tiles on them. These are either ones the user creates themselves or they are taken from a colleague’s Power BI service creation and sharing. It is, in essence, an assortment of different reports and data.
5. Ceramic tiles
Every single piece of visual data kept in the dashboards is referred to as a Tile. To put it another way, the Dashboard is made up of many Tiles.
What Constitutes Power BI’s Principal Elements?
Power BI is comprised on a well-defined architecture comprising many essential components that facilitate its usage. But each of these parts can also be utilized alone as needed. You can also download Acterys Apps for better utilization of Power BI.
The components of Power BI are:
Component #1 – Power BI Desktop
This is the most important part of the Power BI architecture as it is a free program that makes it simple to connect to different data sources, obtain data, transform it, and view the resultant data on a desktop. Additionally, one may produce original designs and photos that they can distribute around the company. This aspect is often utilized and is regarded as the main one.
Component #2: Sources of Data
The sources from which data are gathered for Power BI can be either imported or a live service can be planted to obtain the data. These sources are known as data sources. Because Power BI has a limited amount of storage capacity, the data that is received in both cases are merely compressed versions. But only a select few data sources are supported by Power BI, and they are:
- Online services such as Salesforce reports, Microsoft Exchange Online, Power BI Service, Dynamics 365 (online), SharePoint Online List, and many more.
- Databases from many other sources, including Sybase, Google BidQuery, Snowflake, Oracle, Access, and SQL Server Analysis Services.
- Power BI supports a variety of file types, including JSON, XML, Excel, txt/CSV, and other Sharepoint folder type files.
- Power BI is compatible with several Azure components, including Azure SQL Database, Azure Table Storage, Azure Analysis Services Database (Beta), and many more.
Component #3 Power BI Service
This service is crucial since it provides an internet platform for sharing and publishing reports and converted data in Power BI Desktop. This service uses a web-based platform and adheres to On-Cloud service specifications. One may also use Power BI Service to generate dashboards that are referred to by different names, such as Power BI Web Portal, Power BI Suite, and Power BI Workspace. In addition to these features, it benefits users with Q&A in natural language and alerts for updates and other new improvements. The Free, Pro, or Premium editions of Power BI Services are available to the user.
Component #4 The Power BI Gateway
This is required because, although these gateways assist users in accessing their on-site data sources, the data is not being sent in an extremely safe method. The user may send data to Microsoft Cloud applications such as Power BI, PowerApps, Azure Logic Apps, Microsoft Flow, and others, as well as on premise applications, by using these gateways.
Component #5 Power BI Report Server
Users who own a Power BI Premium license may optimize their usage of Power BI Report Server, which allows them to securely communicate and move dashboards, data, and reports both within and beyond the company.
Component #6: Embedded Power BI
This element is limited to the On-premises Service offered by Azure. This component’s job is to give users access to APIs so they may include dashboards and reports into their own applications.
Component #7 Power BI Mobile Applications
This makes it easier for people to obtain data directly from their mobile devices. Power BI is compatible with Windows, iOS, and Android.
Component #8: Power BI Inquiry
This part improves data connection by giving customers the ability to gather and reorganize data from several platforms and data sources to suit their specific business needs. The SDK connection, which Power BI Query utilizes to operate, is what enables even its third-party connectors to create their own data connectors.
Component #9: Power Pivot
This may be utilized as the foundation for creating a data model and is accessible from an Excel workbook. After data has been maximally compressed, it can also be utilized as a storage area. Power Pivot may be used to load the aggregated and computed data, either directly or with the assistance of Power Query. This is comparable to the tabular model’s SSAS [SQL Server Analysis Services] as well.
Component #10: Power View
This part simply offers a “drag-and-drop” feature that enables users to quickly create different kinds of visualizations in their Excel workbooks using the Power Pivot data model. Additionally, interactive is the nature of these visualizations.
Component #11: Maps of Power
These maps are meant to draw attention to the variations found in the numerical or pictorial data. Colors and the strength of their tones serve to illustrate these contrasts. Overall, Power Maps offer a data visualization tool with characteristics similar to those of a three-dimensional geographic tool.
Component #12: Q&A on Power
It is this component that allows users to ask inquiries and get answers in their native language.
Component #13: Power BI.com Web page
The analyzed data that is supplied online might be stored on this website either as a host or as a cloud.
Because Power BI’s components may be used both alone and in combination, a large user base supports them. Its adaptability boosts productivity and helps users handle and share both large and little amounts of data.
Final Words
Power BI is a noteworthy and vital technology that lets users gather, manage, edit, and distribute data via a cloud-based platform. The diverse constituents of Power BI exhibit distinct functionalities, contributing to its overall efficacy. To boost their effectiveness and functions, these parts can be combined, though. Power BI Desktop, a combination of Power Pivot, Power Query, and Power View, is one such instance. Because they combine to form Power BI, its components play an equally significant role in the tool’s success if Power BI is a dominating force in the corporate sector.
ALSO READ: A Comprehensive Comparison of Google Tasks and Microsoft To-Do