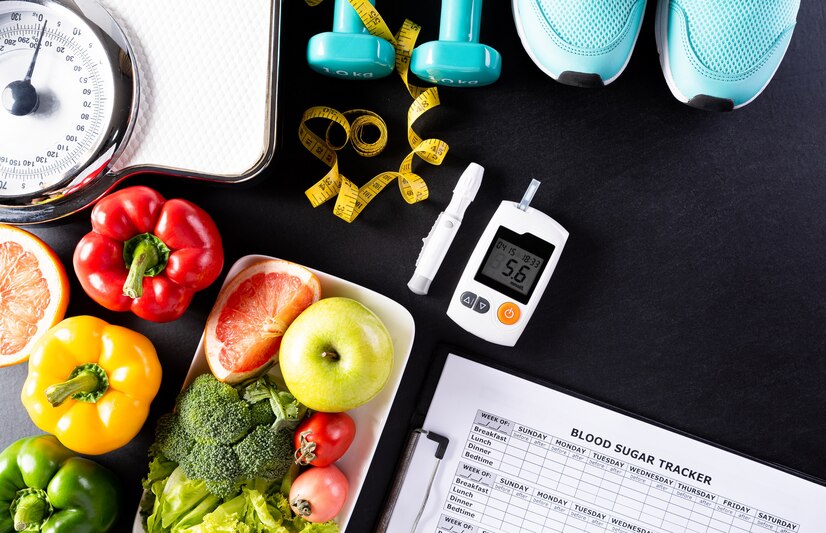
Diabetes, a chronic condition affecting millions globally, has a substantial impact on lifestyle choices, particularly in terms of physical activity and exercise. For individuals living with diabetes, integrating exercise into their daily routine is more than just a health recommendation; it is an essential element in effectively managing their condition. Regular physical activity is crucial in regulating blood glucose levels, enhancing overall health, and minimizing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. This article delves into the complex relationship between diabetes and exercise. It provides valuable insights into the most beneficial exercises for individuals with diabetes, how to create a balanced exercise plan, important safety precautions to consider, and strategies for addressing common challenges faced in maintaining an active lifestyle. For more information on this topic, click here.
Understanding Diabetes
A comprehensive understanding of diabetes forms the foundation for effectively managing it through exercise.
Types of Diabetes and Their Differences
Diabetes is broadly classified into two types: Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes, often diagnosed in children and young adults, is an autoimmune condition where the body does not produce insulin. Type 2 diabetes, more common in adults, is characterized by the body’s inability to use insulin effectively. Understanding these differences is crucial for tailoring an exercise program that addresses specific needs and challenges.
How Diabetes Affects the Body
Diabetes primarily affects the body’s ability to process glucose, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Over time, uncontrolled diabetes can lead to various complications, including heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision problems. Regular physical activity is vital to managing blood sugar levels and preventing these complications.
The Role of Exercise in Blood Sugar Control
Exercise significantly controls blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and helping the muscles absorb glucose more effectively. This process helps lower blood glucose levels, reduce the need for medication, and mitigate the risk of complications.
Benefits of Exercise for Diabetics
The benefits of exercise in diabetes management are manifold and extend beyond just blood sugar control.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity
Regular exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, meaning the body can use insulin more effectively to convert glucose into energy. This improvement is particularly beneficial for individuals with Type 2 diabetes, as it can help manage or even prevent the condition.
Cardiovascular Health and Weight Management
Exercise contributes significantly to cardiovascular health by improving circulation, reducing the risk of heart disease, and aiding in weight management. Maintaining a healthy weight is particularly important for people with diabetes, as obesity is a significant risk factor for developing Type 2 diabetes.
Mental Health Benefits
Physical activity is also linked to improved mental health. Exercise releases endorphins, elevating mood, reducing stress, and enhancing overall well-being. This aspect is crucial, as diabetes management can often be overwhelming and stressful.
Recommended Exercise Types
A balanced exercise regimen for diabetics should include a mix of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility workouts.
Aerobic Exercises
Aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming, are highly recommended for people with diabetes. These activities help improve cardiovascular health, enhance insulin sensitivity, and manage weight. People with diabetes should aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous aerobic exercise per week.
Strength Training
Strength training exercises, such as weight lifting, resistance bands, or bodyweight exercises like push-ups and squats, help build muscle mass. Increased muscle mass is beneficial as it improves metabolism and the body’s ability to manage blood sugar levels.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises
Incorporating flexibility and balance exercises, such as yoga and Tai Chi, can improve joint mobility, reduce the risk of falls, and enhance overall physical function. These activities are particularly beneficial for older adults with diabetes.
Creating a Balanced Exercise Plan
Developing a well-rounded exercise plan is essential for achieving the full benefits of physical activity in diabetes management.
Setting Realistic Goals
Setting achievable and realistic exercise goals is critical to maintaining motivation and consistency. Goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Incorporating Variety and Consistency
A varied exercise routine can prevent boredom and enhance overall engagement with physical activity. Consistency in exercising is crucial for long-term diabetes management and overall health improvement.
Tracking Progress and Adjustments
Regularly tracking progress can provide motivation and help identify areas needing adjustment. An exercise diary or fitness app can effectively monitor and adjust the exercise plan.
Safety Precautions and Considerations
Safety should always be a priority when exercising, especially for individuals with diabetes.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise is essential to prevent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Understanding how different types of exercise affect blood sugar levels can help make necessary adjustments.
Managing Medication and Nutrition Around Exercise
Adjusting medication doses and meal plans around exercise times may be necessary to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Consulting with a healthcare provider for personalized advice is recommended.
Recognizing and Handling Hypoglycemia
Being aware of the signs of hypoglycemia, such as dizziness, shaking, or sweating, and knowing how to handle it (like having a carbohydrate snack handy) is essential for safe exercise.
Overcoming Challenges and Staying Motivated
Staying motivated can be challenging, but various strategies can help maintain a regular exercise routine.
Dealing with Exercise Barriers
Identifying and addressing barriers to exercise, such as lack of time, resources, or motivation, is essential. Finding creative solutions, like short but frequent exercise sessions or home workouts, can help overcome these barriers.
Finding Motivation and Support
Staying motivated can be easier with support from friends, family, or exercise groups. Setting small, achievable goals and celebrating milestones can also boost motivation.
Success Stories and Inspirational Examples
Reading or listening to the success stories of other diabetics who have successfully managed their condition through exercise can be inspiring and motivational. These stories can provide practical tips and demonstrate the positive impact of exercise on diabetes management.
Role of Healthcare Professionals in Guiding Exercise Plans
Having a healthcare team on your side is invaluable when managing diabetes with exercise. These professionals can offer tailored advice, taking into account your overall health, medication regimen, and specific diabetes challenges.
Personalized Exercise Recommendations: Healthcare providers can help you design an exercise program that suits your needs, considering any diabetes-related complications like neuropathy or heart issues. They can also suggest adjustments to your medication or diet to accommodate your physical activity.
Regular Health Check-Ups: Regular check-ups are essential to monitor your diabetes management and adjust your exercise plan. During these visits, discuss your exercise routine and any challenges you face.
Educational Resources: Healthcare professionals can provide educational resources about the benefits of exercise in diabetes management and tips for safe and effective workouts.
Integrating Exercise Into Daily Life
Integrating exercise into your daily routine can be challenging, but with the right strategies, it’s certainly achievable.
Incorporating Physical Activity Into Daily Tasks: Look for opportunities to add more activity to your day, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator, walking during your lunch break, or doing household chores.
Setting a Regular Exercise Schedule: Consistency is vital in managing diabetes. Set a regular schedule for your workouts and stick to it. Whether it’s a morning jog, a midday walk, or an evening bike ride, find a time that works best for you and make it a part of your daily routine.
Fun and Enjoyable Activities: Choose activities that you enjoy. Exercise doesn’t have to be monotonous; dancing, playing a sport, or engaging in outdoor activities can make your exercise routine more enjoyable and sustainable.
Technology and Diabetes Management
Technology can play a significant role in managing diabetes, especially in tracking and improving your exercise regimen.
Fitness Trackers and Apps: Wearable devices and fitness apps can help you monitor your physical activity, track your progress, and set exercise goals. Many apps also offer personalized workout plans and can sync with your glucose monitoring devices.
Online Exercise Programs: There are numerous online resources and programs specifically designed for people with diabetes. These programs can provide guidance and support for home workouts, especially when access to gyms or outdoor spaces is limited.
Telehealth Services: Telehealth services can be beneficial for remote consultations with your healthcare team. These services allow you to discuss your exercise routine and diabetes management without needing in-person visits.
Challenges in Exercise and Diabetes
While exercise is beneficial for diabetes management, it comes with challenges that need to be navigated carefully.
Dealing with Low Energy Levels: Diabetes can sometimes lead to fatigue, making it hard to stay active. Addressing dietary needs, ensuring adequate sleep, and starting with low-intensity exercises can help overcome this challenge.
Exercise-Induced Hypoglycemia: One of the significant concerns for people with diabetes, especially those on insulin therapy, is the risk of hypoglycemia during exercise. To prevent this, monitor your blood glucose levels before, during, and after exercise, and have a carbohydrate-rich snack handy if needed.
Adapting to Physical Limitations: For those with diabetes-related complications such as neuropathy or retinopathy, adapting your exercise routine to accommodate these limitations is essential. Low-impact activities like swimming or cycling can be good options.
Success Stories and Community Support
Hearing about others’ success stories can be incredibly motivating. Many people with diabetes have found ways to integrate exercise effectively into their lives and have seen significant improvements in their health.
Finding Inspiration in Success Stories: Look for stories of individuals who have successfully managed their diabetes through exercise. These stories can provide practical tips and demonstrate the transformative power of physical activity.
Community Support Groups: Joining a diabetes support group, whether in person or online, can provide a sense of community, shared experiences, and mutual encouragement. These groups can also be a source of information and inspiration.
Participating in Diabetes Awareness Events: Community events like charity walks, runs, or cycling events for diabetes can boost your motivation and help you stay committed to your exercise routine.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes through exercise is a balancing act that requires understanding, commitment, and adaptation. By working with healthcare professionals, integrating physical activity into their daily lives, leveraging technology, and drawing inspiration from the community, individuals with diabetes can significantly enhance their quality of life and health outcomes. Remember, the journey of diabetes management is personal and unique to each individual. What works for one person may not work for another, so finding an exercise routine that fits your lifestyle and preferences is essential. With perseverance and the right approach, exercise can become a rewarding and integral part of managing diabetes.
ALSO READ: How to Control Diabetes for Optimal Health and Well-Being